In the previous article, the main computer peripherals were considered. If you have not read it, I recommend that you read it before reading this article. I also recommend reading about how to use the site. Today we will climb into the "holy of holies": system unit or " sistemnik"in everyday life. To make it clear, I disassembled my own system unit and took photographs, which I will provide to you as a visual aid, let's say, system unit device in pictures. Let's start with internal device of the system unit and then move on to the outside. Let's get started!
System blocks are available in various shapes and sizes. While the central processing unit interprets and executes the basic instructions that control the computer. The processor significantly affects the overall computing power and controls most computer operations.
Whether you are a home user or a business user, chances are you will purchase new computer or upgrade your existing computer in the future. Thus, you must understand the purpose of each component in a computer. A computer includes devices used for input, processing, output, storage, and communication. Many of these components are part of the system unit.
To begin with, it is worth mentioning that the system unit in shape can be horizontal (called Desktop), which is usually located under the monitor, or vertical, which is called Tower (c English "tower"). The Tower case, depending on the size, can be big, midi and mini. The most common case is the mini tower, you can just see it in the photographs. By the way, you can check out device of the system unit of your personal computer, however, you need to be very, very careful and first completely de-energize the computer, and only then start doing something. It is advisable to disconnect all the wires, but if there are problems with connecting them, then it is better not to. We will talk about connecting devices to the system unit in a series of articles, having dealt with the external connectors of the system unit. If the system unit needs to be removed from under the table, for example, then this must be done very carefully, avoiding shocks and shocks. To see what is in the system unit, I need to remove the side cover by unscrewing 2 screws on the back wall, however, the case design can be very diverse. The main thing is to carefully examine the case and understand what the cover is attached to. It should be removed without much effort, so do not be zealous. So, the cover is removed, let's figure out what is needed for what.
The system unit is the case that contains the electronic components of the computer used for data processing. The case of the system unit is made of metal or plastic and protects the internal electronic components from damage. All computers and mobile devices have a system unit. On desktop personal computers, electronic components and most storage devices are part of the system unit.
The central processing unit interprets and executes the basic instructions that control the computer. On a personal computer, all of the processor's functions are usually located on a single chip. Some computer and chip manufacturers use the term "microprocessor" to refer to a personal computer's processor chip. Most processor manufacturers now offer multi-core processors. The processor core contains the circuitry needed to execute instructions. The operating system treats each processor core as a separate processor.

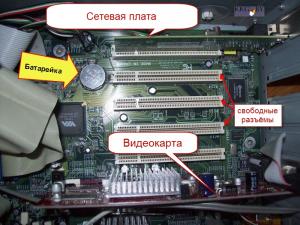
Let's start with system board , which is also called maternal, and sometimes even affectionately "mother." And no wonder: she is the largest and (as befits a mother) monitors a horde of other devices and coordinates their work, transmits a signal from one to another. It is not difficult to find it, the motherboard, as I said, is large. In the photo, it is highlighted with a green frame and marked with the number (1) in the corner.
A multi-core processor is a chip with two or more separate processor cores. The two conventional multi-core processors are dual-core and quad-core. A dual-core processor is a chip that contains two separate processor cores. Similarly, a quad-core processor is a chip with four separate processor cores.
Each processor core on a multi-core processor typically runs at a lower clock speed than a single-core processor, but multi-core processors typically increase overall performance. For example, while a dual-core processor does not double the processing speed of a single-core processor, it can approach those speeds. Multi-core processors are also more energy efficient than individual processors, requiring lower power consumption and less heat in the system unit.
Under the number (2) the processor is hidden in the system unit. He is really hiding, because in the photo he is not visible at all. However, it looks like this:

- This is a specially grown silicon stone, in which, moreover, there are an incredibly many other elements: transistors that are interconnected. The processor is a kind of "brain", because it processes the incoming information. One of its most important characteristics is the clock frequency, which is the number of the simplest (elementary) operations it can perform per unit of time (second). It is measured in MHz (megahertz - that is, in millions of hertz) or GHz (gigahertz - billions of hertz). A lot, right? You can usually see these numbers in the description of the purchased computer or in the sales announcement. For example 3000 MHz. The most common processor brands are Intel and AMD. During operation, the processor heats up, so it is installed on it radiator, which removes all this heat, and is also installed on top cooler- This is a small fan that drives air and cools the radiator. Just you see it under the number (2), and under it a radiator is noticeable. Let's look again at a larger photo:
And other ports and expansion boards are connected to the motherboard directly or via cables. Expansion cards used in some older systems are called daughter cards. The motherboard also has expansion slots, capacitors, power and data connections, fans, heatsinks, and screw holes.
Systems located on the motherboard
Desktop motherboards, cases, and power supplies come in a variety of sizes. All three must be compatible in order to work properly together. Motherboards vary greatly in terms of the types of components they support. Also, some graphics cards, hard drives, and others may not be compatible. The motherboard manufacturer should provide clear guidance on component compatibility.
![]()
The computer operates with information, so it must be stored somewhere. Let's draw an analogy with a person: there are things that we need only during work, for example, a formula. It is not necessary for us to remember it, and it is impossible to keep everything in our heads, so it is written somewhere in a book or in notebook. So is a computer: it stores all data on drives, and when some data is needed for work and needs to be used, it loads it into RAM(RAM - random access memory). She is number (3) in the group photo. It loads because it is faster to work with it, because this memory is very fast. When the computer is turned off, there is nothing in this memory, everything is erased, just like ours, when we sleep - we cannot think at this time. And at this time, the information on the computer is only on the drives.
In laptops and tablets, and even desktop PCs, the motherboard often includes the functions of a video card and a sound card. This helps keep these types of computers small. However, it also prevents upgrades to built-in components.
Physical description of the motherboard
Weak cooling mechanisms on the motherboard can damage Hardware connected to it. Devices connected to the motherboard are often manually installed to make them work with the operating system. On the desktop, opposite the most easily accessible side.
Under the designations (7a) and (7b) and highlighted in yellow, just hard drives . The hard disk is also called hard drive, and in everyday life "screw" or "broom". It stores data even when the computer is turned off. They are characterized by many parameters, but you only need to keep in mind the volume, which shows how much data can be written there, and the access speed. However, it is worth getting acquainted with the units of measurement of information in a separate article, while we omit it. Let's look at Winchester closer from the inside.
It attaches securely through small screws through pre-drilled holes. The front of the motherboard contains ports to which all internal components connect. Several slots allow you to connect one or more memory modules. The other ports are on the motherboard and this allows the hard drive and optical drive connect via data cables.
Power from the power supply is fed to the motherboard using a specially designed port. Also on the front of the motherboard is a number of peripheral card slots. These slots are where most graphics cards are sound cards and other expansion cards connected to the motherboard.

We can also see the cables. Naturally, each device needs electricity, so each has a power cable from power supply, which will be discussed below. And also you can see such a wide cable, in the picture it is signed as “IDE cable”. Do not be afraid, you should only know that there is an IDE hard drive and SATA, it depends on how they are connected to motherboard , we will not go into details, but the latter has a much narrower cable. Information is transmitted through this cable.
Video card: visual representation
Magnetically coded safety switches are interlocking devices that serve to protect people and machines. They are used in comparison with electromechanical safety switches when. The tamper-resistant coded system has been specifically designed to monitor moving machine parts and disable safety devices.
Cooling for processors
Control head of the drive Evaluation unit. . Several permanent magnets are housed in the drive housing. The number of magnets and their location in the housing and the magnetic field strength of individual magnets characterize the type of drive. Therefore, they are also called coded drives.
Thus, we found out that there is RAM, into which data is loaded as needed when the computer is running from drive where it is permanently stored. However, when the computer turns on, it needs commands, because its RAM is empty! Imagine that you wake up and your head is empty! To do this, the computer has Read Only Memory (ROM). It contains basic programs that check the state of the system and its readiness for operation and make it possible to interact with the monitor, hard drive, keyboard, disk drive. All these programs form basic input-output system (BIOS - Basic Input Output System). When you turn on the computer, you immediately see the operation of this most basic system: these are those white letters and numbers on a black background.
The coding of the individual drives in the series is identical. If only one type of drive is used in the machine or the whole system, the service can be exchanged without much administrative effort in case of service. The principle of operation of reed contacts, the number of built-in reed contacts and their spatial arrangement determine the appropriate type of read head. The contact tongues of the reed contacts are closed by the magnetic field of the respective actuator.
Associated drives and readheads are available in 4 different housings. Depending on the application, the user can use them in a cubic or cylindrical design. The read head responds only to the corresponding counterpart, i.e. each type of read head is assigned a specific actuator. The same applies to assigning a read head to an evaluation unit.
If you paid attention, then even if the computer is turned off for a long time, the date and time remain correct. This is due to another microchip CMOS, in which this data and data about the computer hardware are stored, the microcircuit willingly transfers this data on demand to the BIOS, after which the computer boots up. The motherboard has battery, thanks to which no data is lost in CMOS. It lasts for a couple of years, sometimes you have to change.
The evaluation block is a system block below the read head. It switches the safety circuit through internal relays depending on the position of the reed contacts. An exact description of the respective units of value is given in the following sections of the product.
In order to achieve a certain level of security, disadvantages must be taken into account if security-relevant components are used. Possible cause failure is, for example, a cross connection in the connecting line or welding of the reed in the closed position. In the case of a coupled reed contact, the magnetic force may not be sufficient to open the contact. For security reasons, the reader has several reed contacts.

In this picture, you can just see 2 sticks of RAM and a free slot for another one. The bar is simply inserted there and clamped on the sides with holders. You can see them in the picture, they are white, and in the general photo they are numbered (3). On the left, under the lower bar of RAM, there is just a processor heatsink and part of the cooler is visible above it.
If the drive is included in the response range of the read head, the magnets are used to switch the reed contacts. Typically, open contacts are assigned differently polarized magnets. If this is not the case, the safety contacts of the evaluation unit do not switch and the device switches to the blocking state.
The read head is attached to the fixed part of the security device and is connected to the evaluation device via a 2-wire or 4-wire cable. When the safety device is closed, the drive moves into the read head. As soon as the drive is within the response range, the reed contacts switch in the read head, i.e. they change their contact position.
Let's look further, what's interesting inside system unit of a personal computer. Here in the next photo you can see this battery, thanks to which time passes on the computer even if it is turned off. The photo shows the connectors into which you can insert other useful devices.
If the evaluation unit detects a certain position of the reed contacts, i.e. all actuators are in the operating range, the protective contact is released. If the actuator is removed from the readhead, the magnetic field around the reed contacts decreases with increasing distance. When the switch-off distance is reached, the reed contacts return to their preloaded position.
The sensitivity of the reed contacts and the field strength of the magnets determine the switching distance between the drive and the read head. The technical data sheets for actuators and readheads show diagrams of typical response ranges of individual encoder units. For perfect positioning, the read head is positioned in the middle of the response range. The drives and the read head have a large response range. The advantage is that the size of the door gap can be adjusted depending on the response range.
For example, at the top of this photo you see a network board. In the general photo, she is numbered (5). It is needed so that you can connect several computers together so that they can exchange information with each other.
Below you see video card (video adapter), she is number (4) in the general photo. It is needed in order to form and display an image on the monitor.
If the drive moves the read head from the side, short switching distances can be expected. For more information on approach speed, please refer to individual product descriptions. Magnetic systems are characterized by a high degree of protection and a compact design.
Therefore, they are particularly suitable for areas where cleaning or contamination plays an important role. This property allows the system to be used especially in the food industry. However, depending on the material and wall thickness of the shell, switching distances are reduced. Drives and readheads can be connected to a tamper-proof security device using the supplied security screws made of stainless steel material.

Of course, there may not be such a bracket, the video card can be built into the motherboard, but if you need a much better image, if you need to be able to play modern games, then of course the capabilities of the built-in video card are not enough. The video card has its own memory, like RAM. And also powerful video cards have their own heatsink and cooler, because these hard workers also heat up great.
Bit The abbreviation for "binary digit" is the smallest information block in the binary system that corresponds to a memory location. The bit can be 0 or 1. 8 bits are combined into one byte. Bitmap or bit-based graphics. In this case, the computer independently performs the operations that the operating system loads and prepares them for the application by the user.
Boot disk. On the drive from which the kernel is loaded operating system. In addition to this boot program, the boot record contains the partition table for the volume. A corrupt boot record can have serious consequences! Mistake English term"bug" or "bug" is the name for a program bug.
In one of these free slots could be installed and sound card However, I have it built into the motherboard. Sound engineers and music lovers, and everyone who loves high-quality sound, of course, get such a card.
Don't ignore this important device How power unit. Number (6) on the general scheme and right in front of you in the next photo.

This massive comrade is engaged in the distribution of energy between all devices. The power, of course, must be stable, and the unit must be powerful. I have 300 watts, but the computer is quite old. Now there is more power, because there are also needs. The system unit even has its own cooler. We will see it in the next article, where we look at the "appearance" of the system unit.
And finally, we still have several devices that also allow you to save information on drives.

CD/DVD drive. Number 9 in the general photo and close-up right above this text. It allows you to write and read information using a laser on disks. They will be discussed in more detail in the article about information storage. It also comes with a power cable and a cable through which information is transmitted. The main characteristic is the data reading speed.
In some places on the computers there were still oblong slots in front of the system unit. This is a floppy disk drive (FDD). Floppy disks are no longer used almost anywhere due to their low capacity (that is, they contain little information).


So, a blitz inspection of the insides computer system unit finished. We close its cover, screw the screws, it's time to connect everything back and get to work!
So, from this article you learned:
- what they look like and what they are for system unit components
How the system block is arranged what is inside it
Institute of Technology
Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution
higher professional education
"Southern Federal University" in Taganrog
Faculty of Management in Economic and Social Systems
Department of State and Municipal Law and Management
abstract
"Internal devices of the computer system unit"
Performed by a student MZ-70 Rudenko E.I.
checked Tyushnyakov V.N.
Taganrog 2011
Target.
The purpose of writing this essay is to study the internals of the computer system unit and their main properties and characteristics. Also get basic knowledge about the functioning of some elements.
General information.
The system unit is the main node inside which the most important components are installed. Devices that are inside the system unit are called internal, and devices connected to it from the outside are called external. External additional devices designed for input, output and long-term storage of data are also called peripheral.
By appearance system blocks differ in the shape of the case. Personal computer cases are produced in horizontal (desktop) and vertical (tower) versions. Cases with a vertical design are distinguished by dimensions: full-sized (big tower), medium-sized (midi tower) and small-sized (mini tower). Among cases that have a horizontal design, there are flat and extra flat (slim).
In addition to the shape, a parameter called the form factor is important for the case. The requirements for hosted devices depend on it. Former housing standard personal computers was the L G form factor, currently ATX form factor cases are mainly used. The form factor of the case must necessarily be consistent with the form factor of the main (system) board of the computer, the so-called motherboard (see below).
Personal computer cases are supplied with a power supply, and thus the power of the power supply is also one of the parameters of the case. For mass models, the power supply of 250-300 W is sufficient.
Internal devices of the system unit
Motherboard
The motherboard is the main board of a personal computer. It contains:
- processor - the main chip that performs most of the mathematical
and logical operations; - microprocessor set (chipset) - a set of chips that control the operation of the internal devices of a computer and determine the main functionality of the motherboard;
- tires - sets of conductors through which signals are exchanged between
internal devices of the computer; - random access memory (random access memory, RAM) - set
chips designed for temporary data storage when the computer is turned on; - ROM (Read Only Memory) is a microchip designed to
for long-term data storage, including when the computer is turned off; - connectors for connecting additional devices (slots).
The devices included in the motherboard will be considered separately.
HDD
HDD - the main device for long-term storage of large amounts of data and programs. In fact, this is not one disk, but a group of prefabricated disks that have a magnetic coating and rotate at high speed. Thus, this "disk" does not have two surfaces.
Above each surface is a head for reading and writing data. At high disk rotation speeds (90-250 rpm), an aerodynamic cushion is formed in the gap between the head and the surface, and the head hovers above the magnetic surface at a height of several thousandths of a millimeter. When the strength of the current flowing through the head changes, the strength of the dynamic magnetic field in the gap changes, which causes changes in the stationary magnetic field of the ferrimagnetic particles that form the disk coating. This is how data is written to the magnetic disk.
The read operation occurs in reverse order. Magnetized coating particles moving at high speed near the head induce self-induction EMF in it. The electromagnetic signals that arise in this case are amplified and transmitted for processing.
Work management hard drive performs a special hardware-logical device - hard disk controller. In the past, it was a separate daughter board, which was connected to one of the free slots on the motherboard. At present, the functions of disk controllers are partially integrated into the HDD, and are partially performed by microcircuits included in the microprocessor kit (chipset).
floppy disk drive
Information on a hard drive can be stored for years, but sometimes it needs to be transferred from one computer to another. Despite its name, a hard drive is a very fragile device that is sensitive to overloads, shocks and shocks. Theoretically, it is possible to transfer information from one workplace to another by transferring a hard drive, and in some cases they do, but still this technique is considered low-tech, since it requires special care and certain qualifications.
For quick transfer small volumes information is used by the so-called floppy disks(floppy disks), which are inserted into a special drive - drive. The drive inlet is located on the front panel of the system unit. The correct feeding direction of the floppy disk is marked with an arrow on its plastic cover.
The main parameters of floppy disks are: technological size (measured in inches), recording density (measured in multiples) and full capacity.
First computer IBM PC(the ancestor of the platform) was released in 1981. It was possible to connect an external drive using single-sided floppy disks with a diameter of 5.25 inches to it. The disk capacity was 160 KB. The following year, similar double-sided discs with a capacity of 320 KB appeared. Beginning in 1984, high-density 5.25-inch (1.2 MB) floppy disks were produced. These days, 5.25-inch drives are not used, so the production and use of the corresponding drives has practically ceased since the mid-90s.
3.5" floppy disks have been produced since 1980. Single sided disc regular density had a capacity of 180 KB, double-sided - 360 KB, and two hundred double density ronny - 720 KB. 3.5" wheels are now standard. high density. They have a capacity of 1440 KB (1.4 MB) and are marked with the letters HD ( high density - high density).
CD drive CD - ROM
During the period 1994-1995, 5.25-inch floppy disk drives were no longer included in the basic configuration of personal computers, but instead the installation of a disk drive was considered standard. CD - ROM , having the same external dimensions.
Abbreviation CD - ROM ( Compact Disc read - Only Memory ) translated into Russian as posto clear storage device based on CD. The principle of operation of this device is to read numerical data using a laser beam reflected from the surface of the disk. Digital recording on a CD differs from recording on magnetic discs in a very high density, and a standard CD can store approximately 650 MB of data.
Large amounts of data are typical for multimedia information(graphics, music, video), so the drives CD - ROM referred to as multimedia hardware. Software products distributed on CDs are called multimedia publications. Today, multimedia publications are gaining an ever stronger place among other media. traditional types publications. So, for example, there are books, albums, encyclopedias and even periodicals (electronic magazines) published by on CD - ROM .
The main disadvantage of standard drives CD - ROM is the impossibility of recording data, but in parallel with them today there are also CD burners - disk drives CD - RW . For recording, special blanks are used. Some of them allow only one-time recording (after burning, the disc turns into a regular CD CD - ROM , read-only), others allow you to erase previously recorded information and re-record.
The main parameter of drives CD - ROM is the data read speed. It is measured in multiples. The unit of measurement is the speed of reading music CDs, which, in terms of data, is 150 Kb / s.
Video card (video adapter)
Together with monitor video card forms video subsystem personal computer. The video card has not always been a PC component. At the dawn of the development of personal computing, in the general area of \u200b\u200bRAM, there was a small dedicated screen memory, into which the processor entered the image data. Special screen controller read data on the brightness of individual points of the screen from memory cells of this area and, in accordance with them, controlled the sweep of the horizontal beam of the monitor's electron gun.
With the transition from black and white monitors to color and with the increase permissions screen(the number of dots vertically and horizontally) the video memory area became insufficient to store graphic data, and the processor could no longer cope with the construction and updating of the image. Then there was a selection of all operations related to screen management, in a separate block, called video adapter. Physically, the video adapter is made in the form of a separate subsidiary fees, which is inserted into one of the motherboard slots and is called video card. The video adapter has taken over video controller, video processor and video memory.
During the existence of personal computers, several video adapter standards have changed: MDA (monochrome)] CGA (4 colors)", EGA (16 flowers); VGA (256 flowers). Currently used video adapters SVGA , providing selectable playback of up to 16.7 million colors with the ability to randomly select a screen resolution from a standard range of values (640x480, 800x600, 1024x768, 1152x864; 1280x1024 pixels and beyond).
Screen resolution is one of the most important parameters video subsystems. The higher it is, the more information can be displayed on the screen, but the smaller size each individual point and, accordingly, the smaller the visible size of the image elements.
Sound card
The sound card was one of the most recent improvements in the personal computer. It is installed in one of the motherboard connectors as a daughter card. and performs computational operations related to the processing of sound, speech, music. The sound is played through external speakers connected to the output of the sound card. A special connector allows you to send an audio signal to an external amplifier. There is also a microphone jack that allows you to record speech or music and store it on your hard drive for later processing and use.
The main parameter of the sound card is the bit depth, which determines the number of bits used when converting signals from analog to digital form and vice versa. The higher the bit depth, the lower the error associated with digitization, the higher the sound quality. Minimum requirement today are 16 bits, and the most common are 32-bit and 64-bit devices.
In the field of sound reproduction, standardization is the most difficult. In the absence of uniform centralized standards, devices that are compatible with the device have become the de facto standard. sound blaster , trademark owned by the company Creative Labs .
Recently, sound processing has been considered as a relatively simple operation, which, due to the increased power of the processor, can also be assigned to it. In the absence of increased requirements for sound quality, you can use integrated sound systems in which sound processing functions are performed by the central processor and motherboard chips. In this case, the speakers or other audio playback device is connected to the sockets installed directly on the motherboard.
Systems located on the motherboard
RAM
RAM ( RAM - Random Access Memory ) - it is an array of crystalline cells capable of storing data. There are many different types of RAM, but in terms of the physical principle of operation, they distinguish dynamic memory ( DRAM ) and static memory ( SRAM ).
Dynamic memory cells ( DRAM ) can be represented as microcapacitors capable of accumulating charge on their plates. This is the most common and economically available type of memory. The disadvantages of this type are connected, firstly, with the fact that transient processes are inevitable both during charging and discharging capacitors, that is, data recording is relatively slow. The second important drawback is related to the fact that the cell charges tend to dissipate in space, and very quickly. If the RAM is not constantly “recharged”, data loss occurs after a few hundredths of a second. To combat this phenomenon, a constant regeneration (refresh, recharge) memory cells. Regeneration is carried out several tens of times per second and causes waste of computing system resources.
Static memory cells ( SRAM ) can be represented as electronic trace elements - triggers, consisting of several transistors. The trigger does not store the charge, but the state (on/off), therefore, this type of memory provides higher performance, although it is technologically more complex and, accordingly, more expensive.
Dynamic memory chips are used as the main RAM of a computer. Static memory chips are used as auxiliary memory (so-called cache memory) designed to optimize the performance of the processor.
Each memory cell has its own address, which is expressed as a number. In most modern processors, the address limit is typically 32 bits, which means there can be 2 32 independent addresses in total. One addressable cell contains eight binary cells in which 8 bits can be stored, i.e. one byte of data.
Thus, in modern computers possible direct addressing to a memory field of size 2 32 bytes = 4 GB. However, this does not mean at all that this is the amount of RAM that must be in the computer. The maximum size of the RAM field installed in the computer is determined by the microprocessor kit (chipset) motherboard and usually cannot exceed a few GB. The minimum amount of memory is determined by the requirements of the operating system and for modern computers is 128 MB.
An idea of how much RAM should be in a typical computer, is constantly changing. In the mid-80s, a 1 MB memory field seemed huge, in the early 90s 4 MB was considered sufficient, by the mid-90s it increased to 8 MB, and then to 16 MB. Today, 256 MB of RAM is considered typical, but the upward trend continues.
RAM in a computer is located on standard sockets called modules. RAM modules are inserted into the appropriate slots on the motherboard. If there is convenient access to the connectors, then the operation can be performed by hand. If there is no convenient access, incomplete disassembly of the system unit nodes may be required, and in such cases, the operation is entrusted to specialists.
The main characteristics of RAM modules are the amount of memory and the data transfer rate. Today, modules with a volume of 128-512 MB are most common. The baud rate determines the maximum memory bandwidth (in MB/s or GB/s) in the optimal access mode. This takes into account the memory access time, bus width and additional features such as the transfer of multiple signals per cycle. Modules of the same volume can have different speed characteristics.
Sometimes as a defining characteristic of memory is used access time. It is measured in billionths of a second. (nanoseconds, not). For modern memory modules, this value can be 5 ns, and for especially fast memory, used mainly in video cards, it can drop to 2-3 ns.
CPU
The processor is the main microcircuit of the computer, in which all calculations are performed. Structurally, the processor consists of cells similar to RAM cells, but in these cells data can not only be stored, but also changed. The internal cells of the processor are called registers. It is also important to note that data in some registers is considered not as data, but as commands that control the processing of data in other registers. Among the processor registers there are those that, depending on their content, are able to modify the execution of commands. Thus, by controlling the sending of data to different registers of the processor, it is possible to control the processing of data. This is what programs are based on.
With other computer devices, and primarily with RAM, the processor is connected by several groups of conductors, called tires. There are three main tires: data bus, address bus and command bus.
address bus. For processors of the family Pentium(namely, they are most common in personal computers) the address bus is 32-bit, that is, it consists of 32 parallel conductors. Depending on whether there is voltage on one of the lines or not, they say that one or zero is set on this line. The combination of 32 zeros and ones forms a 32-bit address pointing to one of the RAM cells. The processor is connected to it to copy data from the cell to one of its registers.
Data bus. This bus is used to copy data from RAM to processor registers and vice versa. In modern personal computers, the data bus, as a rule, is 64-bit, that is, it consists of 64 lines, along which 8 bytes are received at once for processing.
Command bus. In order for the processor to process data, it needs instructions. It must know what to do with those bytes that are stored in its registers. These commands come to the processor also from RAM, but not from those areas where data arrays are stored, but from where programs are stored. Commands are also represented as bytes. The simplest commands fit into one byte, but there are also those that require two, three or more bytes. Most modern processors have a 32-bit instruction bus, although there are 64-bit processors and even 128-bit ones.
Processor instruction set. During operation, the processor serves the data in its registers in the RAM field, as well as the data in external ports processor. It interprets part of the data directly as data, part of the data as address data, and part as commands. The set of all possible instructions that the processor can execute on data forms the so-called processor instruction set. Processors belonging to the same family have the same or similar instruction systems. Processors belonging to different families differ in instruction system and are not interchangeable.
Processors with extended and reduced instruction sets. The wider the set of system commands of the processor, the more complex its architecture, the longer the formal instruction record (in bytes), the higher average duration execution of a single instruction, measured in processor cycles. So, for example, the command system of processors of the family Pentium currently has over a thousand different teams. Such processors are called extended system processors my commands - CISC -processors ( CISC - Complex instructions set Computing ).
In contrast to C / SC processors, processors of the architecture appeared in the mid-80s RISC with abbreviated command system ( RISC - Reduced instructions set Computing ). With this architecture, the number of instructions in the system is much smaller and each of them is executed much faster. Thus, programs consisting of the simplest instructions are executed by these processors much faster. The downside of the abbreviated instruction set is that complex operations have to be emulated by a far from efficient sequence of the simplest abbreviated instructions.
As a result of the competition between the two approaches to processor architecture, the following distribution of their areas of application has developed:
CISC processors are used in mainframe computing systems;
RISC processors are used in specialized computing systems
or devices focused on performing uniform operations.
Platform personal computers IBM PC focused on the use of CISC-processors.
Processor compatibility. If two processors have the same instruction set, then they are fully compatible at the software level. This means that a program written for one processor can be executed by another processor. Processors with different systems commands are generally incompatible or only partially compatible at the software level.
Processor groups having limited compatibility are considered as processor families. For example, all processors Intel Pentium belong to the so-called family x86. The ancestor of this family was a 16-bit processor Intel 8086, on the basis of which the first model of the IBM PC was assembled. Subsequently issued Intel processors 80286, Intel 80386, Intel 80486, several Intel Pentium models] several Intel Pentium MMX models, Intel Pentium Pro models, Intel Pentium II, Intel Celeron, IntelXeon, Intel Pentium III, Intel Pentium 4, and others. All these models, and not only them, as well as many models of processors from AMD and some other manufacturers belong to the x86 family and have top-down compatibility.
The principle of "top-down" compatibility is an example of incomplete compatibility when each new processor "understands" all the commands of its predecessors, but not vice versa. This is natural, since twenty years ago, processor designers could not provide the instruction set needed for modern programs. Thanks to this compatibility, on a modern computer, you can run any programs created in recent decades for any and previous computers belonging to the same hardware platform.
Basic parameters of processors. The main parameters of processors are: operating voltage, bit depth, operating clock frequency, internal clock multiplier and cache size.
The processor is based on the same clock principle as in conventional clocks. The execution of each command takes a certain number of cycles. In a wall clock, the pendulum sets the oscillation cycles; in manual mechanical watches, they are set by a spring pendulum; in an electronic clock, for this there is an oscillatory circuit that sets the cycles of a strictly defined frequency. In a personal computer, clock pulses are set by one of the microcircuits included in the microprocessor kit (chipset) located on the motherboard. The higher the frequency of clocks received by the processor, the more commands it can execute per unit of time, the higher its performance. First processors x86 could
work with a frequency not higher than 4.77 MHz, and today operating frequencies some processors are already exceeding 3 billion cycles per second (3 GHz).
ROM chip and system BIOS
At the moment the computer is turned on, there is nothing in its RAM - no data, no programs, since RAM cannot store anything without recharging cells for more than hundredths of a second, but the processor needs commands, including at the first moment after turning on. Therefore, immediately after switching on, the starting address is set on the address bus of the processor. This happens in hardware, without the participation of programs (always the same). The processor turns to the exposed address for its first command and then starts working on programs.
This source address cannot point to RAM, which has nothing in it yet. It points to another type of memory - permanent memory of the mouth Roystvo (ROM). The ROM chip is capable of storing information for a long time, even when the computer is turned off. Programs in ROM are called "hardwired" - they are written there at the stage of manufacturing the microcircuit.
Bus interfaces of the motherboard
Communication between all native and connected devices of the motherboard is carried out by its buses and logical devices located in microcircuits microprocessor set(chipset). The performance of the computer largely depends on the architecture of these elements.
ISA. Historic achievement of platform computers IBM PC was the introduction almost twenty years ago of an architecture that received the status industrial standard ISA ( Industry standard architecture ). It not only allowed to connect all the devices of the system unit with each other, but also provided a simple connection of new devices through standard connectors (slots). The bandwidth of a bus made according to this architecture is up to 5.5 MB / s, but, despite the low bandwidth, this bus can still be used in some computers to connect relatively "slow" external devices such as sound cards and modems.
EISA. Standard extension ISA became the standard EISA ( Extended ISA ), characterized by an increased connector and increased performance (up to 32 MB / s). Like ISA , this standard is now considered obsolete. After 2000 release motherboards with connectors ISA / EISA and the devices connected to them, is practically discontinued.
VLB. The name of the interface translates as local bus standard VESA ( VESA Local Bus ). The concept of " local bus first appeared in the late 80s. It is due to the fact that with the introduction of processors of the third and fourth generations ( Intel 80386 and Intel 80486) frequency of the main bus (the bus was used as the main IS A / EISA ) was not enough for the exchange between the processor and RAM. The local bus, which has an increased frequency, interconnected the processor and memory, bypassing the main bus. Subsequently, an interface for connecting a video adapter, which also requires increased bandwidth, was "embedded" into this bus - this is how the standard appeared VLB , which made it possible to raise the local bus clock speed to 50 MHz and provide a peak throughput of up to 130 MB / s.
The main disadvantage of the interface VLB became that the limiting frequency of the local bus and, accordingly, its bandwidth depend on the number of devices connected to the bus. So, for example, at a frequency of 50 MHz, only one device (video card) can be connected to the bus. For comparison, let's say that at a frequency of 40 MHz, it is possible to connect two, and at a frequency of 33 MHz - three devices. Active tire use VLB did not last very long, it was soon forced out by the tire PCL
PCI. Interface PCI ( Peripheral Component Interconnect - connection standard external components) was introduced in personal computers at the time of the 80486 processor and the first versions Pentium . At its core, this is also a local bus interface that connects the processor with RAM, into which connectors for connecting external devices are embedded. To communicate with the main computer bus ( ISA / EISA ) special interface converters are used - bridges PCI ( PCI Bridge ). Bridge functions in modern computers PCI perform chips of a microprocessor set (chipset).
This interface supports a bus frequency of 33 MHz and provides a throughput of 132 MB/s. The latest versions of the interface support frequencies up to 66 MHz and deliver 264 MB/s for 32-bit data and 528 MB/s for 64-bit data.
An important innovation implemented by this standard was the support for the so-called mode plug - and - play , later developed into an industry standard for self-installing devices. Its essence is that after the physical connection of an external device to the bus connector PCI there is an exchange of data between the device and the motherboard, as a result of which the device automatically receives the number of the interrupt used, the address of the connection port and the number of the direct memory access channel.
Conflicts between devices for possession of the same resources (interrupt numbers, port addresses and direct memory access channels) cause a lot of problems for users when installing devices connected to the bus ISA . With the advent of the interface PCI and with the design of the standard plug - and - play it became possible to install new devices using automatic software tools- these functions were largely assigned to the operating system.
FSB. The PC/ bus introduced in processor-based computers Intel Pentium as a local bus, designed to connect the processor with RAM, did not remain in this capacity for long. Today it is used only as a bus for connecting external devices, and for connecting the processor and memory, starting with the processor Intel Pentium Pro , a special tire is used, called Front side Bus ( FSB ). This bus operates at a frequency of 100-200 MHz. Bus frequency FSB is one of the main consumer parameters - it is he who is indicated in the specification of the motherboard. Modern types memory ( DDR SDRAM , RDRAM ) capable of transmitting multiple signals per bus cycle FSB , which increases the speed of data exchange with RAM.
AGP. A video adapter is a device that requires a particularly high data transfer rate. As with local bus implementation VLB , and when implementing a local bus PCI the video adapter has always been the first device to be "cut" into the new bus. When the tire parameters PCI ceased to meet the requirements of video adapters, a separate bus was developed for them, called A GP ( Advanced Graphic port - improved graphics port). The frequency of this bus is the same as the PC/ bus (33 MHz or 66 MHz), but it has a much higher bandwidth due to the transmission of several signals per clock cycle. The number of signals transmitted in one cycle is indicated as a multiplier, for example A GP4x (in this mode, the transfer rate reaches 1066 MB / s). latest version tires A GP has a multiplicity of 8x.
PCMCIA ( Personal computer Memory card International Association - standard of the International Association of Manufacturers of Memory Boards for Personal Computers). This standard defines the interface for connecting small flat memory cards and is used in portable personal computers.
USB ( Universal Serial Bus - universal serial bus). This is one of the latest innovations in motherboard architectures. This standard defines the way a computer interacts with peripheral equipment. It allows you to connect up to 256 different devices with a serial interface. Devices can be switched on in chains (each next device is connected to the previous one). Tire performance USB relatively small, but quite sufficient for devices such as a keyboard, mouse, modem, joystick, printer, etc. The convenience of the bus is that it virtually eliminates conflicts between various equipment, allows you to connect and disconnect devices in a "hot mode" (without turning off the computer) and allows you to combine several computers into a simple local network without the use of special equipment and software.
PCI-E ( Peripheral Component Interconnect - Express - connection standard external components) - appeared quite recently, its main role is to replace AGP as it can no longer cope with the video data stream. transfer rate exceeds 2100 MB/s
Conclusion
Based on the results of writing the essay, the following conclusions can be drawn: the system unit is a very complex device, which is the main element in the computer architecture. Consisting of a large number separate and often integral elements. All computational processes take place in the system unit. And absolutely all the peripherals of the computer are connected to it.
Used Books
1. Encyclopedia for children. T. 14. Technique / Chapter. ed. M. D. Aksyonova. - M.: Avanta +, 1999 - 688 p.: ill.
2. Encyclopedia for children. Volume 22. Informatics / Chapter. ed. E. A. Khlebalina, Ved. scientific ed. A.G.Leonov.- M.: Avanta+ 2003.-624p.: ill.
3. www.ixbit.com
4. Computer science. Basic course. For universities 2nd edition / Ed. S. V. Simonovich. SPb.: Piter, 2007. -640s.: ill.
