purpose of work : experimental study of network configuration in the operating system Windows 7 .
Work tasks :
Familiarize yourself with the Network and Sharing Center component.
Understand the concept of network location.
Familiarize yourself with the Network Map component.
Familiarize yourself with the network components of the operating system required to connect your computer to a local or external network.
All categories are presented and then the differences are presented in a table. When you connect to new network, you are prompted to select it. The following four network sites are available. This is the right choice for a private network, such as a home. They know the people and devices that participate in the network and consider them trustworthy. Network discovery is enabled in this configuration. This means that you can see and see other computers on the network. In addition, the file and printer are activated. This allows other members to use other resources, such as files and printers on the network.
Prepare a progress report.
THEORETICAL DATA
Often, setting local network in operating systems Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008/2008 R2 starts with a network property configuration area called the Network and Sharing Center component. With this network configuration tool, you can select a network location, view a network map, configure network discovery, general access to files and printers, and to configure and view the status of your current network connections.
home network provides an additional feature. This makes it easy to share files and printers. Group members just need to enter a password to join the group. This category is intended for small networks of companies. The only difference with a home network is that no home network group can be created or merged.
You should always use the public network on public hotspots. This category provides the highest security setting. Network discovery, file sharing, and home network group are disabled. The firewall blocks all related data packets. Thus, your computer is not visible to others. If you are connecting directly to the Internet, without a router, you must also select this option.
Opening the Network and Sharing Center component
In order to use the functionality of the network configuration tool, you must first open it. To open the Network and Sharing Center window, do one of the following:
R 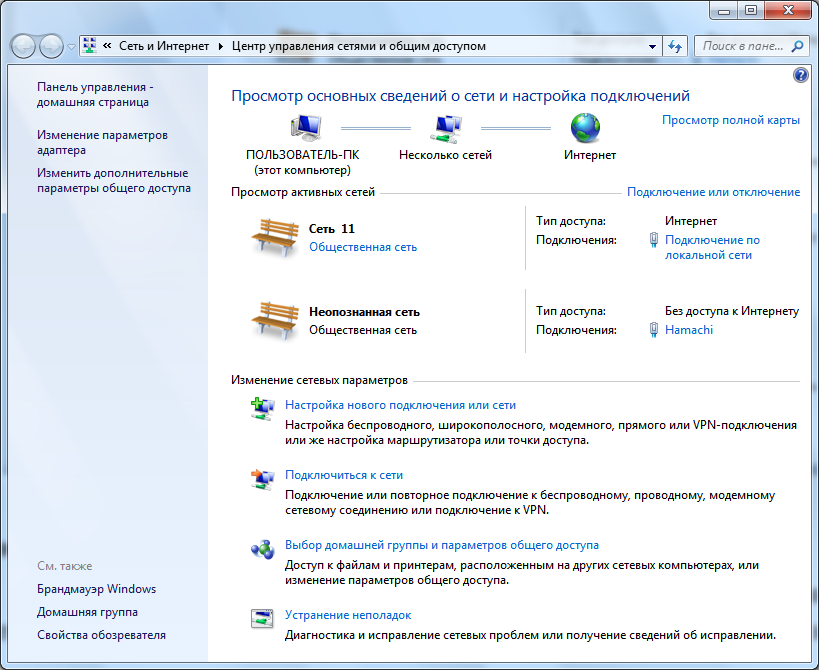 is. 1.1. "Network and Sharing Center"
is. 1.1. "Network and Sharing Center"
This network location is used for workstations in medium to large enterprises and cannot be directly selected. Administration is carried out through the domain administrator of the corresponding domain network. If you don't know which network location you should choose, choose a public network.
Then you must determine the correct network location. This is especially useful when connecting to other networks. By choosing the right location, you can ensure that your computer is always set to the appropriate security level.
- Your computer is invisible to other computers in this area.
- You cannot see other computers and devices on the network.
Concept of network location
Before you start working with this component, you should understand such a concept as a network location. This setting is set for computers the first time they connect to a network, and during connection, firewall and security settings are automatically configured for the type of network to which they are connecting. Unlike the Windows Vista operating system, which uses the most restrictive network hosting firewall profile for all network connections, Windows 7 supports multiple active profiles, which allows for the most secure use of multiple network adapters connected to different networks. There are four types of network location (Figure 1.2).
- Other users on the network can also see your computer.
- You can also browse other computers and devices on the network.
A structural representation of your network is also possible. However, the problem can be solved very easily. Double-click the download file and follow the instructions on the screen: Click Run.
- Accept the license agreement and click Next.
- Wait until the installation completes and click Finish.
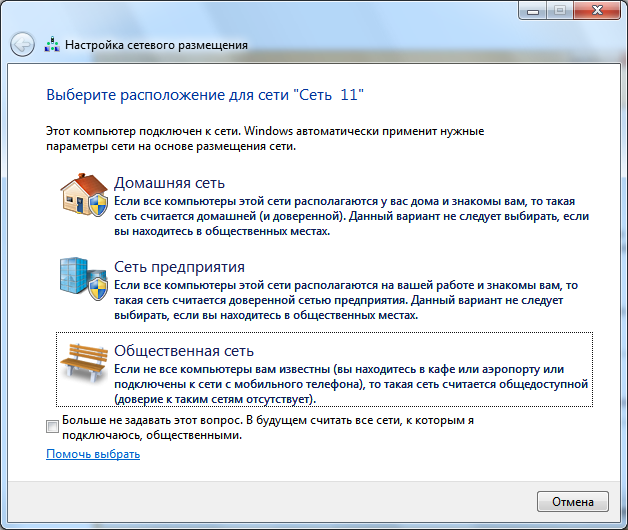
Rice. 1.2. Choosing a network location
Home network. This network location is intended for use at home or on networks where users know each other very well. These computers can create and join homegroups. For home networks, network discovery is automatically enabled.
Some network analysis objects are records that provide raw table data for analysis. They are only included in the analysis layer for the vehicle routing problem. Other network analysis objects are functions that contain both geographic location and tabular data. However, most network analysis objects are network sites that have table data, geographic location, and position in relation to the network dataset.
The following section details network locations. A network location is a special type of network analysis object that is connected to a network and whose location is used on the network as an input to the analysis. Such as a stopover may only be located at a specific location in the network, while other network sites, such as a line barrier for imaging sites, may contain an area of one or more edges.
Enterprise network. This network location is used in a small office (SOHO) network. This network location also has network discovery enabled, but you can neither create nor join a computer to a homegroup.
Public network. This network location is for using the computer in public places such as cafes or airports. This is the most restrictive placement and has homegroup joins and network discovery turned off by default.
If the network location is a single point, its location in the network is determined by four network fields in the attribute table.
- This value is stored as a ratio.
- This field is limited to two values: right side and left side.
Network Location Example: Route Stops
The following example illustrates how the network location fields work. The two points representing the start and end of the route are loaded as stops in the route analysis layer. Although the points are not directly on the streets, the position with the shortest distance on the network is found and stored as a numeric value in the network's four stop fields. The route analysis is then computed to determine the best route.
domain network. If the computer is joined to an Active Directory domain, then the existing network will automatically be assigned the network location type "Domain". The domain network location type is similar to the work network, except that the configuration in the domain is Windows firewall, network discovery, and the network card is determined by group policy.
The following attribute table represents the associated network fields. The information in the field determines which elements are covered by the object and how much of each edge element is covered. The only network analysis objects that can be more accurately defined as network sites are line barriers and polygonal barriers.
The classification of polygons as line sites may seem misleading. Imagine networks are one-dimensional. Polygons are two-dimensional, but the network can only use parts of the polygons that overlap the network. The properties for incremental tolerance and catch environment help you find the network location for network sites that you add or move. These properties are part of the network analysis layer and are found in the Layer Properties dialog box.
How computers are connected on a network can be viewed using the network map. However, this feature is not available for all network location types.
Network map
A network map is a graphical representation of the location of computers and devices that allows you to see all the devices on your local network, as well as how they are connected to each other. The Network and Sharing Center window displays only the local part of the network card, the layout of which depends on the network connections you have. The computer on which the map is being created is displayed in the upper left corner. Other computers on the subnet appear on the left. Infrastructure devices such as switches, hubs, and gateways to other networks appear on the right. Network mapping works on wired and wireless networks, however, only on private and domain networks. It is not possible to view the public network map. The LLTD protocol ensures that only computers on the same subnet are mapped, which is a common setup in home or small office environments.
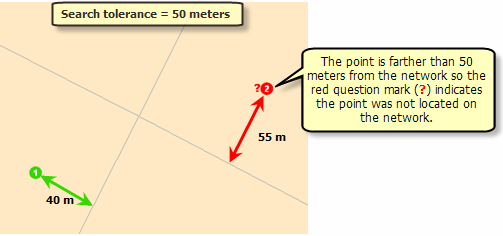
This ensures that the analysis input is online. These settings are used in the following operations. Download locations or add locations Create online locations Copy and paste online locations Move network sites. The standard tolerance is 000 meters. If a point is out of range, the resulting network location is not located, it is not assigned a network position, and it cannot be included in the analysis correctly.
Network add-on areas such as line barriers are independent of drug tolerance. Therefore, they must exactly overlap the network in order to have an impact. In the following chart, 50 meters has been identified as an addiction tolerance. The point was not located because it is more than 50 meters away from all network functions.
M  You may notice that some computers and devices appear separately at the bottom of the Network Map window, or may not appear at all. For example, if the wireless network print server supports UPnP and not LLTD, then it will be located at the bottom of the Network Map window. This situation arises because not all operating systems and devices assume support for the LLTD protocol or due to possible misconfiguration of devices. You can see an example of a network map in Figure 1.3.
You may notice that some computers and devices appear separately at the bottom of the Network Map window, or may not appear at all. For example, if the wireless network print server supports UPnP and not LLTD, then it will be located at the bottom of the Network Map window. This situation arises because not all operating systems and devices assume support for the LLTD protocol or due to possible misconfiguration of devices. You can see an example of a network map in Figure 1.3.
Fishing for network sites
The following figure shows both points, as the higher value was defined for constraint tolerance. 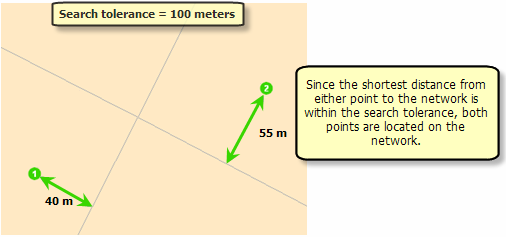
You may want to place stops on a specific source function, such as nodes but not roads, or you may want to place stops on a multimodal network on roads but not rail lines. You can even find them on junctions and, if no junction is found within tolerance, on roads.
Rice. 1.3. Network map example
Two components are responsible for the operation of the network map in operating systems:
Link Layer Topology Discover Mapper (LLTD Mapper) is a component that queries the network for devices to be included in the map;
LLTD (Link Layer Topology Discover Responder - LLTD Responder) responder is a component that is responsible for queries of the LLTD Mapper component.
The network nodes of a point are always located directly on the network, even if the symbols used for display are not located there. Network location fields describe the exact location of an object on the network. There you can enable location snapping along the network snap and assign any offset. If the network dataset has more than one source, you can specify which source class classes to use to find the network element. To find the nearest NE across multiple sources, click Next and select one of the fields in the Start table for each search to search.
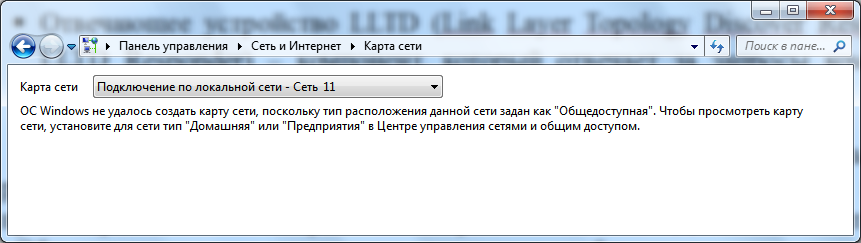
By default, the network map can only be viewed for Home Network or Enterprise Network locations. When you try to view the network map for the "Domain network" or "Public network" locations, you will see a message that the map cannot be displayed.
You can specify for each source whether the network location should be the nearest point along the function, in the middle of the function, or at the end of the function. Disabled sources are not scanned. If, finally, neither the road nor the iron rail element is found, the point will remain uninhabited. You can change the order of the sources in the table. To do this, select the sources and change their sequence using the arrow buttons on the right.
The following figure shows how network sites are located based on the settings in the graph above. You can change these settings to catch nodes by including only one node source. If network sites should always be located on the source feature, for example, in a feature that represents enterprise objects, you can include that source instead.
Rice. 1.4. Trying to view the network map
To enable network mapping on a domain network, you need to do the following on a domain controller:
Open the Group Policy Management snap-in;
Select a GPO (for example, Default Domain Policy, scope - the entire domain) that will be distributed to a computer located in a domain network, click on it right click mice in and out context menu select the "Edit" command;
Cut environment with "Create Query"
You can also define a query to limit the search to a subset of the features in the original feature class. This is recommended if you are not looking for features that are not suitable for your network location. For example, if you want to load polygon points and don't want to place them on local roads, you can define a query that only searches for major roads.
Exclude non-passing parts of the network
If you enable this option, network sites will only be hosted on passing parts of the network. This prevents network objects from being placed on items that cannot be reached due to constraints or barriers.
Fishing environment and net locations
For network localization areas, such as line barriers, the capture environment defines the source feature classes that contain the network analysis objects. The dependency tolerance is ignored because the localization areas of the network are constrained by the elements they overlap.In the Group Policy Management Editor snap-in, expand Computer Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/Network/Link Topology Detection (Link Layer) and select the Enable I/O Display Driver (LLTDIO) policy;
In the properties of the policy setting, set the radio button to the option "Enable" and check the box "Allow operation for the domain";
Control questions and tasks for self-training
If you have two feature class classes "Streets" and "Railways" and deactivate "Railways", any added line or polygon barriers are located only on roads, even if the barriers cover rail lines. When you create a network location, the network site fields are calculated using a spatial lookup.
If you are loading network sites that have already been localized, the site fields contain all the data required for the new location. In this way, values from the network location fields can be copied and relatively slow spatial lookups can be avoided.
Repeat the same steps for the "Enable Responder Driver (RSPNDR)" policy setting;
Update the policy settings on the client machine using the gpupdate /force /boot command;
Update the network map.
Network connections
After installing the driver for each network adapter, the Windows operating system attempts to automatically configure network connections on local computer. All available network connections are displayed in the Network Connections window. A network connection is a set of data required to connect a computer to the Internet, a local network, or any other computer.
You can open the Network Connections window in any of the following ways:
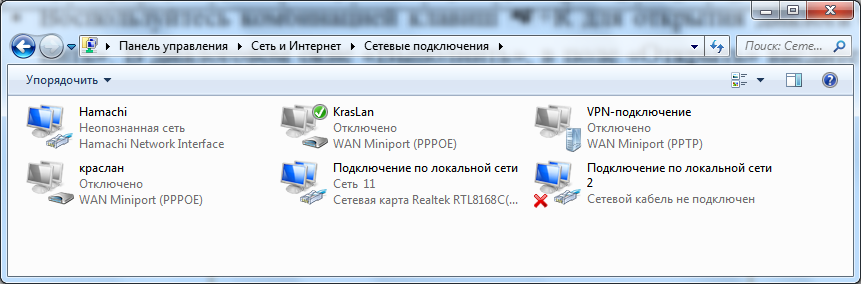
Rice. 1.5. Network Connections window
When you select any network connection, you can perform the following actions with it:
Renaming a connection. Operating system names all network connections "Local Area Connection" or "Wireless Network Connection" and a connection number by default if you have more than one network connection. If desired, you can rename any network connection in one of the following three ways:
Press the F2 key, enter a new name for the network connection, and then press the Enter key;
Right-click on the one to be renamed network connection and select "Rename" from the context menu. Enter a new name for the network connection, then press the Enter key;
Select a network connection and click on the "Rename connection" button, which is located on the toolbar. Then enter a new network connection name and press the Enter key.
Network status. Using this window, you can view any network connection status and details such as IP address, MAC address, and more. To open the network connection details dialog, do the following:
Open the Status dialog box in one of the following ways:
Right-click on the network connection and select the "Status" command from the context menu;
Select a network connection and click on the "View connection status" button, which is located on the toolbar;
Select a network connection and press the Enter key.
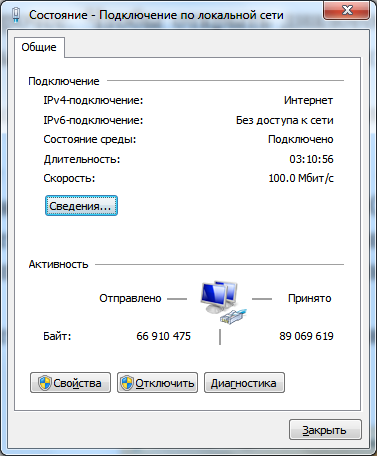
Rice. 1.6. Local Area Connection Status Dialog Box
In the "Status - Local Area Connection" window, click the "Details" button. In the Network Connection Details dialog box shown below, you can view the details of the current network connection.
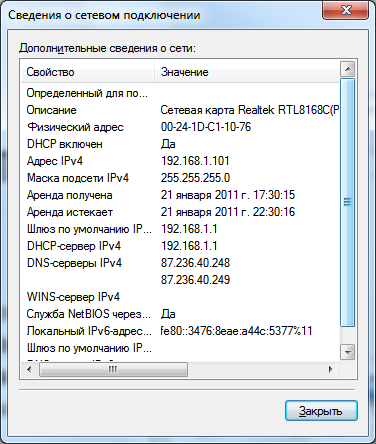
Rice. 1.7. Network connection details
Connection diagnostics. If you find problems with your network connection, the Network Connections window offers a diagnostic tool " Troubleshooting”, which contains the possibility of solving using connection analysis. To use this tool, do any of the following:
Right-click on the network connection and select "Diagnostics" from the context menu.
Select a network connection and click on the "Connection Diagnostics" button, which is located on the toolbar.
In the Windows Network Diagnostics dialog box that opens, follow the steps in the wizard to troubleshoot.
Rice. 1.8. Opening the Local Area Connection Troubleshooter
Disabling a network device. Sometimes problems with network connections are solved by disconnecting the computer's network adapter from the network. In order to disable network adapter Perform one of the following actions:
Right-click on the network connection and select "Disconnect" from the context menu;
Select a network connection and click on the "Disable network device" button, which is located on the toolbar.
Setting connection settings. As such, network connections do not allow communication. The implementation of communications is provided by network clients, services and protocols that are tied to the created network connections (Fig. 1.11.).
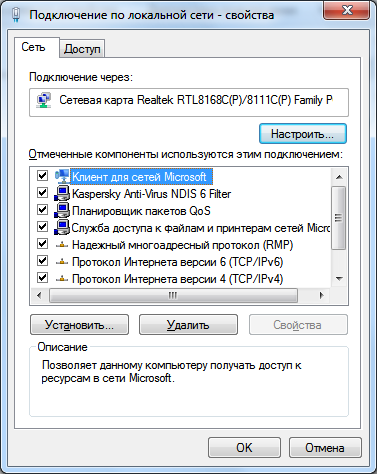
Rice. 1.11. Network Connection Properties Dialog Box
To change your network connection settings, you can use the connection settings tool. To change the components and network connection settings, follow these steps:
Right-click on the network connection and select "Properties" from the context menu;
Select a network connection and click on the "Configure connection settings" button, which is located on the toolbar;
Select a network connection and use the combination Alt keys+ Enter.
The checkboxes next to the components indicate that these components are bound to the connection.
Thus, within the framework of this laboratory work, the means for configuring the network properties of operating Windows systems- Network and Sharing Center. The concepts of network location, network cards are considered, with the help of which the local part of the network card is displayed, the layout of which depends on the available network connections. You also got acquainted with the network connections window, which allows you to configure network connections on the local computer. In the next lab, you will learn how you can configure clients, services, and network connection protocols using the GUI.
CONTROL QUESTIONS AND TASKS FOR SELF-EDUCATION
What is the purpose of the Network and Sharing Center component?
Demonstrate the ways to open the Network and Sharing Center component.
Describe the types of network location.
What is a network map, in fact, and in appearance?
What protocols are responsible for building a network map.
In what situations will it not be possible to view the network map?
What network hardware component is associated with the properties of available network connections?
What are the ways to open the Network Connections window?
What actions can a user typically take on any network connection?
Describe the properties of the network connection information for the computer on which you are performing the lab. Explain the meaning of these properties.
What are the ways to call the connection diagnostics tools?
Describe the components of connection to computer network, for which you are doing the lab.
When connecting to the network for the first time you must select a network location. This will automatically detect the firewall and security settings for the type of network you want to connect to.
If you connect to networks in multiple locations (for example, at home, at a local coffee shop, or at work), choosing a network location can ensure that your computer is always set to the appropriate security level.
Exists four types of network locations:
- Select home network for home networks or where trust exists between users and devices on the network. Computers on a home network can belong to a homegroup. Find the network, enabled on home networks, allows you to see other computers and devices on the network, and allows other network users to see the current computer.
- Select type Working network for a small office or other work networks. Find the network, allows you to see other computers and devices on the network and allows other network users to see the current computer, is enabled by default.
- Select Shared network for networks in public places (for example, cafes or airports). With this type of location, the computer remains invisible to other computers nearby and protected from any malware from the Internet. home group is not available on shared networks and network search is turned off. This option should also be selected if direct connection to the Internet without a router or a mobile broadband connection.
- network location Domain used for domain networks, in particular corporate work networks. This type of network location is controlled by an administrator. The type cannot be selected or changed.
Note: If you do not want to share files or printers, the safe location type is public network.
Change network location type:
- Open the Network and Sharing Center.
- Select Work network, Home network or Shared network and select the type of network location you want.
Attention! Selecting the type "Home network" or "Work network" changes the firewall configuration to allow communication. This may be a safety hazard.
What makes a home or work network secure
To be sure that your home or work network safe to connect, make sure it has the following components:
- For wireless networks – a wireless connection encrypted using secure WiFi access(WPA or WPA2). (WPA2 is preferred because it is more secure than WPA.)
- For all networks– a firewall or other network address translation (NAT) device connected between the computer or wireless access point and the cable or DSL modem.
Impact of Windows Firewall on network locations
The Shared Network location type blocks certain programs and services from running to help protect your computer from unauthorized access when connected to a network in a shared location. If your computer is connected to a public network and Windows Firewall is enabled, some programs and services may ask you to unblock them (allow communication through the firewall) to ensure they work properly.
When you unblock a program, the firewall unblocks it for every network with the same network location type that your computer is currently connected to. For example, if you connect to a network in a coffee shop and select the location type "Shared Network", and then unlock the instant messaging program, the instant messaging program will be unlocked for all shared networks that your computer is currently connected to.
If multiple programs are unlocked when connected to a public network, it is recommended that you change the network location type to "Home network" or "Work network". It may be safer to change this one network than to affect every public network that the computer connects to. But, remember that if you make this change, the computer becomes visible to other users on the network, and this is
