Permanent deletion of information (introduction, data recovery algorithms, methods of deleting information, data destruction standards, source codes).
1. Introduction.
Protecting personal data is a top priority for most organizations and individuals.
It is difficult to imagine what might happen if personal data ( Email, photos, passwords for accessing banking operations, and other important information) will fall into the hands of an attacker, he will know everything that was stored on the hard drive. And the fact that before selling a computer or hard drive you have deleted all personal information or even formatted the hard drive, is not always an obstacle to accessing data.
Erasing files using standard Windows features, you add them to the shopping cart.
After that, with a few clicks of the mouse button, recovering supposedly deleted files is very easy. Even emptying the Recycle Bin won't help: yet free space there is enough space on the disk, the operating system will not overwrite old files with new ones, so deleted files can be recovered with a specialized utility. Even when formatting storage media, such as memory cards or flash drives, only the file allocation table is cleared.
*** Windows includes the cipher.exe utility based on the DOD algorithm. ***

Not all users understand that when a file is deleted, the content of that file is not deleted from the hard drive.
Files are made up of bytes, they remain on the disk, but are no longer associated with file system. The data itself remains on the disk until the operating system reuses the disk space allocated for them to write new data. Even if you format the drive, the data will usually not be deleted. Just the content will be cleared.
In order to delete files for sure, you need to write to the place where it was stored new data. Up to this point, the file can be restored by reading it not through the operating system, but using a special software, commercial data recovery programs or recovering it manually by other methods.
If there was no writing to the sectors containing files, then the data physically remained in their places, but information about their location was lost or distorted. Thus, it is required to determine exactly where the sectors containing necessary information, and count them in the correct order.
2. Data recovery algorithms.
To save data, there are many data recovery programs (the most common are R-studio, GetDataBack, Ontrack EasyRecovery, etc.).
In the general case, data recovery programs first scan the disk, based on the detected service records, map the location of the fragments of the files to be recovered, and build a directory tree. The map contains information about which cluster belongs to which file, sizes, names and other attributes of file system elements. If the information obtained as a result of scanning is not enough, then certain extrapolation methods are used. Then the files and folders that need to be restored are selected in accordance with the compiled map and transferred to another medium.
Basic data recovery algorithms.
- recovery deleted files on a valid file system, a full scan for most types of file systems is not required in such cases, it is used exclusively to recover deleted files, some programs run it automatically during the pre-scan.
- file system reconstruction after damage or formatting, the goal is to create a virtual directory tree that reflects the contents of the scanned file system in its original state, without damage, if successful, you can save the necessary data from there to another partition.
-data recovery by signatures, the so-called "rough" recovery or "raw recovery".
3. Ways to delete information.
There are several ways to delete a file from your hard drive for sure or make it impossible to access it. Some of the ways to prevent this type of data leakage from a hard drive include:
- disk demagnetization;
- data rewriting;
- encoding;
- physical destruction of the carrier.
Destroying important data on a computer hard drive or other media is The best way ensure that valuable data cannot be recovered even in the best computer labs. Destruction is of fundamental importance when moving computers that stored valuable information from a safe place to a less reliable one.
An even more effective approach to deleting data is to demagnetize the hard drive. This method disables the hard drive. But when using it, it will no longer be possible to use the GMD for its intended purpose. (for example, using a special device - Degausser).

If you want to delete data from hard drives or other media and have a guarantee that the hard drive will be usable, you need to use data wipe. This is a good solution for reuse computer in another department of the organization. For example, if a computer in your organization is transferred to a new employee, the data will be deleted, but the computer will still remain in working condition. , Wise Disk Cleaner, etc.).
Another method of getting rid of data is to overwrite all the memory on all sections of the hard disk. One rewriting will be quite enough to be completely sure that the previous information cannot be restored.
It is important to remember that the simple deletion of a file by the operating system only leads to the deletion of the path to the file, digital information when simple removal will be saved on the hard disk. Even re-formatting or dividing a hard disk into sections is not a guarantee that there are no files left. Moreover, the files are saved even if the user cannot see them.
As a last resort, if there is a need to completely delete files without the possibility of recovering them, physical destruction of the storage medium is the best choice. Storage media can be destroyed in several ways, including direct damage to the surface of a magnetic disk or drum with abrasive materials. Corrosive chemicals will give the same results, provided that the surface being written to is completely exposed to attack.
4. Data destruction standards.
GOST P50739-95;
The Russian algorithm GOST R 50739-95 is the recommended time-tested algorithm.
The advantages of the algorithm are fast work, and the disadvantages are that the algorithm does not provide for multiple entries.
According to GOST R 50739-95, it is determined that erasure is performed by writing masking information into it (Section 5.1.5 GOST R 50739-95), but the number of cycles and the content of masking information are not indicated.
It turns out that even after one cycle of writing masking information on the hard drive, for example, by alternating codes of zero and one (0x55, 0xAA), the residual magnetization from the past data remains (aka the effect of residual information) and it can be easily read using special equipment.
DoD 5220.22-M; NAVSO P-5239-26 (RLL);
The standard of the US Department of Defense, which is widely used in the world. A better standard than the Russian GOST R 50739-95, but nevertheless the US military forbade its use to remove classified information.
According to the American standard, erasure is carried out in (E-edition of the algorithm) three cycles:
the first - randomly selected characters are stored in each byte of each sector;
the second - inverted data is written (zero is replaced by one);
the third is the recording of a random sequence;
Such cyclicity provides a low degree of residual magnetization, which makes it possible for special tools to obtain a minimum set of residual information.
In another edition of the algorithm (ECE) - a seven-fold overwrite is used.
In addition to these algorithms defined by government standards, there are a number of algorithms from independent experts in the field information security.
Bruce Schneider.
A world-famous expert, in narrow professional circles, proposed the following seven-step algorithm:
1. Filling with units over the existing data
2. Padding with zeros over existing data
3. Write random data
4. Write random data
5. Write random data
6. Write random data
7. Write random data
No, this is not a mistake, the expert suggests filling the HDD with random data five times. Although, Schneider himself later stated:
"Recent studies.... using tunneling microscopes, have shown that even this may not be enough."
Peter Gutmann.
Gutman proposed an algorithm with many cycles, which are focused on the destruction of records, using equipment that supports MFM / RLL technology (magnetic force recording using coding), when a random sequence of encrypted information of 35 cycles is recorded. Although, Gutman himself in the same article makes a note that manufacturers of new HDDs already support this technology.
This algorithm is considered "paranoid".
VSITR.
German algorithm, which provides for seven times overwriting of data;

Proceeding from data recovery algorithms that recover only "undistorted" information, it is most rational to use data deletion using standard multiple data erasure algorithms, recovery after which is almost impossible.
No one will argue that the protection of information and ensuring information security is the most important task of every enterprise today. It is clear to everyone why it is necessary to keep secret all corporate passwords, access codes, accounting, financial indicators, and other valuable information classified as "trade secret": the leakage of such data very quickly leads to the collapse of the company. However, few people think about the methods of destroying information from obsolete hard drives or flash drives. But in vain! Experts unanimously repeat: simple formatting does not at all guarantee complete deletion of information without the possibility of recovery.
Information protection is the most important task of every enterprise
Simple erasure and software methods: out of sight, out of mind?
It seems to ordinary users that erasing files, and even more so formatting a disk, leads to the complete destruction of data. Is it so? Practice shows that it is not. Simply erasing information from a disk is the most unreliable method of keeping it secret, since in this case it is not the data itself that is erased, but the path to it.
After erasing, the information still remains on the disk, it just loses its connection with the file system, and therefore is not visible to the average user. If we draw analogies, then a formatted disk is like a book from which the content was torn out, leaving the rest of the pages. Even a novice hacker with the help of special recovery programs can easily "reanimate" such a disk and get the entire database stored on it. Safe and sound!

Recovering data "destroyed" by programs for deleting information or simple formatting is easy
Advanced users prefer not the usual formatting, but special programs for deleting information. This decision is justified: it becomes more difficult to restore the disk (especially if you use professional-level programs). But not for professionals.
| Level | Method Essence | Information recovery | Reliability |
| Base | A sequence of zeros is written to the main and backup tables, as well as to the boot sector of the hard disk using special programs. The data is not destroyed, but access to it becomes more complicated. | Maybe. Information is restored in full using software that analyzes disk sectors. | very low |
| Advanced | Sequences of zeros and ones are written to the data sectors: the data and the boot area are destroyed by overwriting. | Maybe. But not for the average user: special skills and special equipment will be required. | average |
| Professional | The same. Only instead of one, several rewriting cycles are carried out in order to “overwrite” the old data as best as possible. | Depends on the number of cycles. The more of them, the less the probability of data recovery. | average |
Advantages software methods:
Disadvantages of software methods:
|
|||
Mechanical destruction of hard drives: through fire and water
So, simple erasure and killer programs do not guarantee complete security. How then to destroy secret data? The first thing that comes to mind is to break or melt HDD. The idea is good: after high-quality disposal, the data will be really impossible to read. The only problem is how to implement it. And how much money will it take.
| Name | Method Essence | Information recovery | Reliability |
| Mechanical | The media is shredded in a special device (shredder). | medium to high | |
| Thermal | The carrier is melted in special furnaces (a temperature of at least 800-1000 °C is required!). | Impossible. | high |
| Pyrotechnic | Explosion destruction. | Perhaps in laboratory conditions (if large disk fragments remain). | medium to high |
| Chemical | Placing the carrier in a chemically aggressive environment. | Impossible. | high |
| Radiation | Treatment with ionizing radiation. | Impossible. | high |
Advantages of mechanical methods:
Disadvantages of mechanical methods:
|
|||
Physical destruction of data
Physical destruction is a great option for those who do not have the funds to rent a smelter or the services of pyrotechnics. The essence of the method is simple: a special device generates a short-term electromagnetic field that magnetizes the hard drive to the limit value (ie, to saturation). As a result, the magnetic domains of the disk are reoriented, and the recorded data is destroyed along with the service markup. And without it, both restoration (at least partial!), And further use of the carrier becomes impossible. Achieved complete removal information from the hard drive - it turns into a useless piece of plastic!
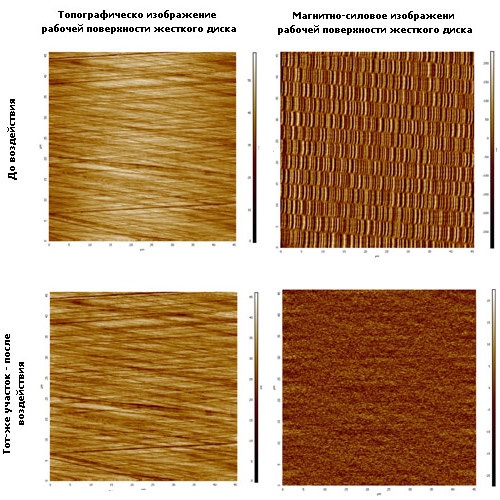

Such information destruction devices are quite inexpensive, and therefore are often mounted directly into hard drives or flash drives. Such media with a self-destruct function is much more convenient and reliable than conventional ones. In addition, they can be destroyed not only after write-off, but also automatically in case of theft. Agree, a valuable ability in our turbulent times!
The only drawback of physical destruction is the impossibility of further recovery and use of the carrier. That is, the irretrievable deletion of information from a flash drive using the system built into it automatically means the destruction of the flash drive itself. However, the disadvantage of the method is at the same time its most important advantage: the media cannot be restored, which means that it will not work to read data from it either.
Thus, the most reliable methods of destruction of information without the possibility of recovery are mechanical and physical. But if the former are associated with high costs and the danger of pollution, then the latter are much more accessible and safer. As for simple erasing and special programs for deleting information, their use is hardly justified: the risk of recovering valuable information is too great.
Instruction
A free program for guaranteed destruction of information on disks, using the US Department of Defense standard (DoD 5220-22.M). A distinctive feature of this application is the ability to generate and print a certificate confirming the operation of permanent deletion of data. Supports OS Windows, MS-DOS, Linux. There is also a paid version.
Another one free utility securely deleting data from disks, as well as individual directories, files, Windows Recycle Bin or unused media space. It is characterized by the presence of many cleaning methods and the possibility of combining them. You can also set and execute the operation according to your own method. Supports operating Windows systems XP SP3, Server 2003 SP2, Vista, Server 2008, 7, Server 2008 R2.
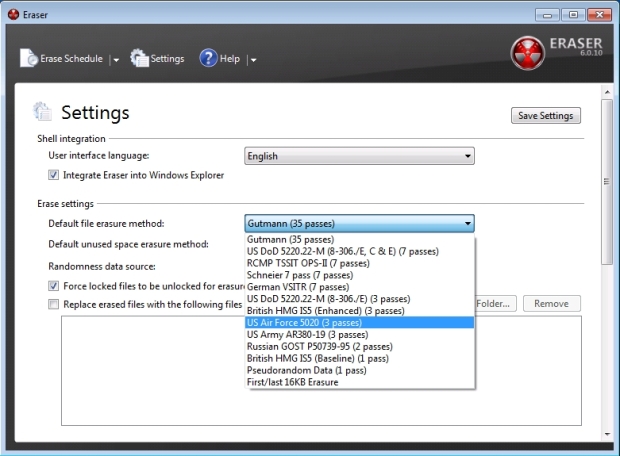
A simple, lightweight, free utility for guaranteed cleaning of hard and USB drives, flash cards. Supports many kill methods including DoD 5220-22.M and Peter Gutmann's method (35 passes). The program does not require installation. Supported Microsoft Windows XP, Vista. It has a size of about 1 MB.

Darik's Boot and Nuke (DBAN). The most popular free program among others for guaranteed destruction of data from various disks. Has an open source. Focused on safety and performance. Supports a large number of erasing methods. Distributed as an ISO image for recording on an optical or USB disk. It does not require an operating system to work.
