Why do you need HDD?
A task hard drive is to store data. Everything on your computer resides on your hard drive. And it's not just about documents, images and videos. Your programs, settings, and even your operating system are all stored on your computer's hard drive.
And all this can be lost at once if the disk is damaged. Such is the reality. That's why most people create a system Reserve copy. They get another hard drive and copy all their important files to it.
What size hard drive do you need?
Everything that can be stored on a hard drive has a size. Text files usually take up little space, images - more, music - even more, and the most "weighty" are video files.
The hard drive is like a scale. He does not "see" the qualitative difference between the stored data, only their weight (size) is important to him. But its hard drive does not measure in meters and kilograms, but in megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB) and terabytes (TB).
Roughly speaking, there are 1 million bytes in a megabyte, 1 billion in a gigabyte, and 1 trillion bytes in a terabyte.
What does this mean for users?
If you often need to transfer files from one computer to another, or if you only want to back up some files, a small hard drive (such as a 500 GB Expansion series drive) will suffice.
If it is necessary to do backup entire computer, or even multiple computers, or you have a lot of video and audio files, you will need a larger drive (such as a 1TB or higher Backup Plus series desktop drive).
Is the hard drive needed for which computer: PC or Mac?
Any Seagate drive is compatible with PCs and Macs. Some discs are sold pre-formatted to work with certain types of computers, but they can always be reformatted as needed.
IMPORTANT NOTE! Reformatting a disk erases every single file on it. Therefore, before performing this action, be sure to save copies of the files to a safe location.
But using one disk with both PCs and Macs is a rather difficult task. In short, they are not compatible. And if a little more, then the possibilities of such use are very limited: it will be possible to perform only certain certain operations in certain special conditions. For more information on this subject, see .
What are the types of hard drive connections?
There are four main ways connecting hard disk to the computer.
- USB
This is the most common type of connection. It does not require any software to be installed. Just plug in the cable. The computer will recognize the drive and you will be able to read and save files almost immediately. - firewire
Equipped with an auto-configuration feature like USB, the Firewire 800 provides high data transfer speeds and is therefore popular with users who frequently transfer video files from one computer to another. - SATA
This is the standard connection type for internal hard drives. It allows you to transfer files of any format at the highest speed. - eSATA
A less common high-performance connection type that is most often used in PC computers. With an eSATA type connection, files are transferred at a speed that is closest to the transfer speed of the internal hard drive.
What does it matter hard speed disk?
When you turn on your computer, open a file, listen to a song, or perform any other activity, you are using the hard drive. Rotating plates are placed inside the disc. The higher the rotation speed, the faster computer finds the file you need.
Therefore, a 7200 RPM drive transfers data faster than a 5400 RPM drive. Your work will be affected differently depending on the type of disc you are using. If the drive is external, you will hardly notice the difference. If the drive is internal, the difference will be felt - and the more pronounced, the larger the files or applications you use.
Which drive to choose: internal or external?
The internal disk provides data transfer at a higher speed. External drive more flexible and expandable storage resources.
Each option has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Internal drives require physical installation, while not every user will decide to open the computer case. But files and programs in this case are stored directly on the computer and are available at any time.
External hard drives connected to the computer using a plug-in cable, such as portable disk Backup Plus Portable, or they are accessed via Wi-Fi, as is the case with the Wireless Plus drive. This allows you to take necessary files take them with you, transfer them to other computers, or increase storage space on your computer or network instantly and without unnecessary technical difficulties.
How much information can be stored?
Here are some averages that will help you get an idea of the storage possibilities on hard drives.
Digital Music (MP3) | Digital photos* | Digital video | DVD quality movies † |
|
500 GB †† | ||||
16,660 hours | 1,000 hours | |||
1.5 TB | 24,990 hours | 1 500 hours | ||
33,320 hours | 2,000 hours |
* Average file size when using the camera's highest resolution in JPEG format. The actual number of images that can fit on the hard disk may vary depending on the camera model and features of the scene being photographed.
† Two-hour DVD-quality movies.
†† One gigabyte (GB) capacity hard disk space is assumed to be one billion bytes. Available capacity may vary depending on operating environment and formatting. Number of stored files for different applications is provided for example only. Actual Quantities depends on many factors, including file size and format, tools used, and software applications.
The hard disk of a computer (aka - HDD (Hard Disk Drive), it's also a hard drive, it's also a magnetic drive, it's also a "screw" and - "hard"). Non-volatile storage of our movie collections and other files :) "Non-volatile" in this case means that all saved information remains on the hard drive after turning off the computer power.
What kind of functions (besides directly storing our data) does a computer hard drive perform? We install all our software on it. Our most important program (a set of programs) is also installed on it - the operating system. Without an operating system, a computer is a pile of expensive hardware, you yourself understand :) A computer hard drive also very often performs another important function, being (if necessary) an extension for random access memory computer. Especially - with a shortage of the latter.
Let me explain with an example: Software, running on a computer and performing some task, it needs 300 megabytes of memory to work, and only 250 megabytes are free at the moment (for example). The operating system makes a tricky move: it begins to "dump" data that has not been requested for a long time from the RAM to the hard drive of the computer, thus freeing up space in the RAM for the needs of the running program.
In fairness, it should be noted that the overall speed of any task in this case begins to fall catastrophically. And this is logical. After all, the speed of memory and hard disk cannot be compared. The hard drive of a computer is much slower, and the more data the operating system has to "dump" on it from fast RAM, the more noticeable the overall performance drop will be.
If this process is taken to extremes, then a situation is possible in which almost any user action will be accompanied by convulsive attempts by the operating system to free the next section of RAM and rewriting the next portion of data to the hard disk. This can be visually determined by the constantly flashing red indicator of the hard drive on the front panel of the computer. The result is a very slow response of the system to any user actions (often resembles a freeze) and a constantly flashing red light (LED) of the hard drive on the front panel of the case.
The situation described above is often computer systems with insufficient RAM. More precisely, let's formulate it this way: with insufficient memory for the tasks that are set for it :)
A few words about the fallacy associated with hard drive computer: many believe that there is a vacuum inside it, but this is not so. During the production cycle, the internal closed disk space (HDA) is filled with air at a pressure of one atmosphere to create an "air cushion" effect between the "pancakes" and the read-write magnetic heads.
The requirements for air purity inside the HDA (containment area) are quite strict. There should not be dust particles larger than 0.3 microns (micrometer or micron). For comparison, the average thickness of a human hair is 40 microns. Now, I think it is clear that a computer hard drive cannot be disassembled at home.
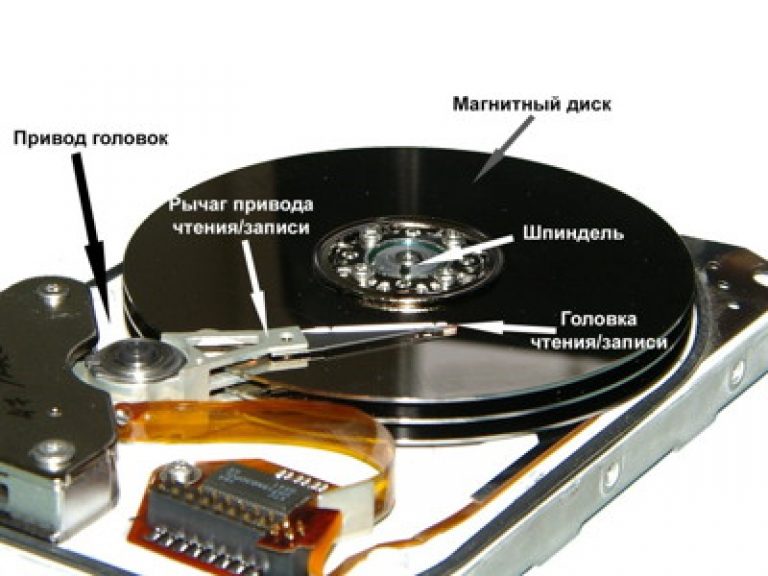
Inside the hard drive there is a spindle (axis), on which one or more "pancake" magnetic disks are strung, which are located one above the other. Under this design is a motor that spins the spindle to the required speed.
The magnetic heads that perform read-write operations in the computer's hard disk are combined into a magnetic head unit (MH), which simultaneously moves them all and places them above the desired hard disk cylinder. The BMG drive is called a positioner.
And now let's "look under the cover" :) So - a computer hard drive without a protective cover.

What do we see here:
- 1 - spindle that spins the hard drive plate.
- 2 - the magnetic plate of the hard disk itself - "pancake" (where all our information is recorded)
- 3 - read-write head, which, moving a few microns from the surface of the disk, performs read-write operations.
If we completely disassemble the hard drive of the computer, we will see this picture:
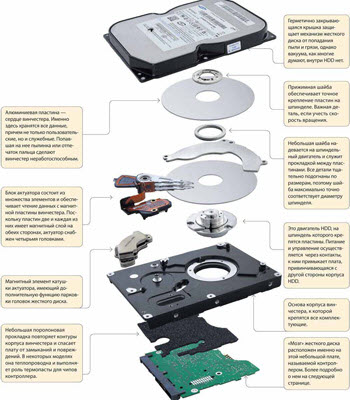
The picture is clickable.
There is another class of devices - external rigid disks. This is, in fact, structurally the same hard drive, only more compact and hermetically packed in an anti-shock shell. Such drives are connected to a computer via a USB interface and act as "large flash drives" :)

There is an opinion that there is a vacuum inside the disk, but this is not so. Each computer hard drive has a special micro-hole, under which (on the inside) there are several filters, they protect the tight area of the hard drive from dust particles from the air entering it.
Now solid-state computer drives are becoming more and more fashionable: SSD - solid-state drive. You can read about my personal acquaintance and experience with SSD drives in a separate article on our website.
Many of you know that all the information on the computer, presented in the form of files and folders, is stored on the hard drive. And here, what is a hard drive and what it is intended for, not many will correctly answer. It is very difficult for people who are far from programming to imagine how information can be stored on some kind of piece of iron. After all, this is not a box or a piece of paper on which this very information can be written down and hidden in a box. Yes, a hard drive is not a box with a letter.
A hard disk (HDD, HMDD-from the English hard (magnetic) disk drive) is a magnetic storage medium. In computer slang, it is called "Winchester". It is designed to store information in the form of photos, pictures, letters, books in various formats, music, movies, etc. Outwardly, this device does not look like a disk at all. Rather, it looks like a small rectangular iron box.

The internals of a hard drive are like an old turntable.

Inside this metal box, there are round aluminum or glass disk plates located on the same axis, along which the reading head moves. Unlike a player, the hard disk head does not touch the surface of the platters during operation.

For convenience, the hard disk is divided into several sections. This division is conditional. This is done using the operating system or special programs. The new partitions are called logical drives. They are assigned the letters C, D, E or F. It is usually installed on the C drive, and the files and folders are stored on other drives so that your files and folders do not suffer if the system crashes.

Watch a video about what a hard drive is:
Key Features of Hard Drives
- Form factor is the width of the hard drive in inches. Standard size for desktop computer 3.5 inches, and for laptops 2.5 inches;
- Interface- in modern computers used to connect to motherboard SATA different versions. SATA, SATA II, SATA III. Older computers use the IDE interface.
- Capacity- it maximum amount information that a hard drive can store is measured in gigabytes;
- Spindle speed is the number of spindle revolutions per minute. The faster the disk spins, the better. For operating systems discs of 7,200 rpm or higher must be installed, and for file storage, you can install discs with a lower speed.
- MTBF is the mean time between failures as calculated by the manufacturer. The larger it is, the better;
- Random access time is the average value of the time required for the head to position on an arbitrary section of the plate. The value is not constant.
- impact resistance is the ability of a hard drive to withstand pressure changes and shocks.
- Noise level, which the disc emits during operation is measured in decibels. The smaller it is, the better.
Already there SSD drives(solid-state drive in simple translation - solid-state drive), which have neither a spindle nor platters. This is a storage device based on memory chips.
