1 year ago

SATA is a specialized interface. He found wide application in order to connect a wide variety of storage media. For example, using SATA cables, you can connect hard drives, SSD drives and other devices that serve to store information.
The SATA cable is a red cable that is about 1 centimeter wide. That's what he's good for, first of all. After all, with such data you can’t confuse it with other interfaces. In particular with ATA (IDE). This interface is also quite applicable for connecting hard drives. And he did a good job with it, but until the SATA interface appeared.
Unlike SATA, the ATA interface is a parallel interface. ATA (IDE) cable consists of 40 conductors. Several such wide loops in system block affect cooling efficiency. This problem was inherent in the ATA interface, which cannot be said about SATA. He has his own advantages. And one of them is the speed of information transfer. Let's say SATA 2.0 can transfer data at 300 MB/s, while SATA 3.0 can transfer as much as 600 MB/s.
Compared to the old ATA (IDE) interface, its advantage is that it has great versatility. Using the SATA interface, it is possible to connect external devices.
To make connecting easier external devices, have developed a special version of the interface - eSATA (External SATA).
eSATA (External SATA) is an interface for connecting external devices that supports hot-plug mode. It was created a little later, in mid-2004. It has more reliable connectors and increased cable length. Due to this, the eSATA interface is convenient for connecting various external devices.
A separate cable must be used to power connected eSATA devices. Today there are bold predictions that in future versions of the interface it will be possible to introduce power directly into the eSATA cable.
eSATA has its own characteristics. The average practical data transfer rate is higher than USB 2.0 or IEEE 1394. SATA and eSATA signaling are compatible. However, they require different signal levels.
It also needs two wires to connect: a data bus and a power cable. In the future, it is planned to abandon the separate power cable for remote eSATA devices. Its connectors are less fragile. Structurally, they are designed for a greater number of connections than SATA. However, they are physically incompatible with conventional SATA. Plus connector shielding.
The length of the cable is brought to two meters. SATA is only 1 meter long. To compensate for the loss compensation, the signal levels were changed in it. The transmit level is raised and the receiver threshold level is lowered.
Despite evolution optical technologies and the emergence of such standards as HD DVD and Blu-Ray, namely hard drives allow those who work with digital media data to store and transfer colossal volumes. The optics are simply not enough to store even ordinary video in the processing stage, not to mention high definition video (High Definition - HD). It's no secret that during processing, to output just one minute of the finished video, you have to store an entire hour of source material, which is then assembled, recomposed and re-folded. Therefore, it is not surprising that many professionals use external drives.
Typically, external hard drives are slower than their internal counterparts. In order not to lose mobility, external drives usually use the USB or FireWire interface, which imposes a limit on the transfer rate: peak throughput ranges from 400 to 480 Mbps. How small this is compared to the new SATA standard, which provides up to 300 Gb / s! And every next year, with the increase in the number of megapixels of cameras and the popularization of HD video, the old interfaces will seem more and more "wretched", because it will take a long time to copy 30 GB of video to a disk with a USB interface. Noticeably longer than the second hard SATA drive if it is installed on your computer.
In addition to high performance, an important advantage of the SATA interface is "hot swap". Today we will introduce you to one of the pioneers among the external hard drives SATA (eSATA): Seagate eSATA 500 GB. It should be noted that although we tested the 500 GB version, Seagate also produces a 300 GB eSATA drive model, which costs accordingly less.

The appearance of the Seagate eSATA drive.
Like all Seagate hard drives, the drive that came to us for testing has a model number. In this case, it is ST3500601XS-RK, which is impossible to remember, and unnecessary. It's easier to call the device Seagate eSATA, and everyone will understand you - even the Price.ru database. Inside the Seagate eSATA is a 7200 RPM Seagate Barracuda ST3500641 hard drive, which is to line 7200.9 with a capacity of 500 GB and 16 MB cache. This is not the last model from Seagate - a 750 GB drive from the 7200.10 family has already been in the THG laboratory, which we are now raffling off among our readers. For the computer to see HDD Seagate eSATA 500Gb, the device must be connected eSATA cable for data transmission and power cable.

eSATA cable is black, red is normal SATA cable. Do not confuse.
The design of eSATA is broadly similar to that of other Seagate hard drives, but there are differences. The stylish silver case with black inserts is made a little differently than the Seagate 400Gb Pushbutton Backup models - both the front panel and the back are different. The changes on the front panel are more cosmetic, but the front button now turns on the drive, rather than launching the utility Reserve copy. After power is supplied to the Seagate eSATA 500Gb, the blue LED lights up. Numerous USB and Firewire connectors have disappeared from the back, and the socket into which the plug from the power supply is inserted has also changed.
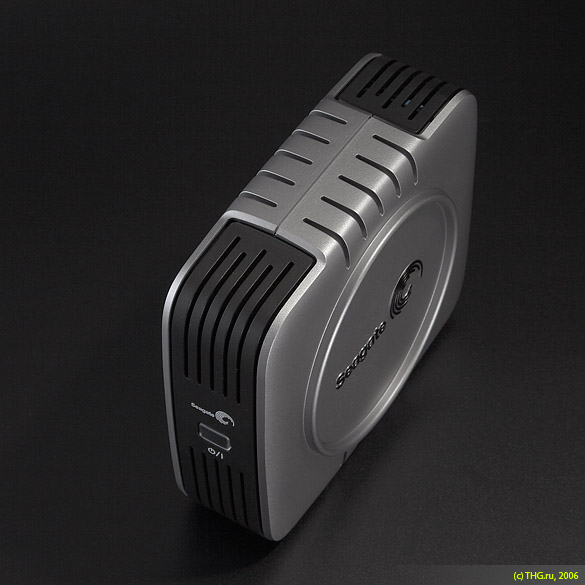

Another nice feature of Seagate external hard drives has also disappeared - the possibility of modular connection. Previous Seagate PushButton Backups could be stacked on top of each other and connected with a FireWire cable "through the other". However, this could not be done with the USB interface. Now we have an eSATA interface, and "one to another" drives are no longer connected. But, now drives can be connected in RAID. And you can put them on top of each other as before, while the design of the cover is optimized so that the "stack" of hard drives does not fall apart.

Only one eSATA connector on the back
The drive comes with a Promise eSATA300 TX2 controller with two external ports. A very logical step, since eSATA ports on motherboards, although they are found, are not as common as USB and FireWire. Note that connecting Seagate eSATA to a laptop is a completely different topic. The laptop controller is not supplied with the device.

The package includes a Promise eSATA300 TX2 PCI controller.
In addition to the drive and eSATA card, the bundle includes the BounceBack Express V 7.0 software package. It is very easy to use and allows you to back up entire drives and folders. In addition, Bounceback gives you the ability to schedule backups. It is true to compare BounceBack with type reservations Acronis True Image Or Norton Ghost, we would not - too different weight categories.
![]()
User manual and cables included.
As we have noted, the key difference between the new Seagate eSATA drive and older hard drives is that the drive has lost its FireWire and USB ports. In our opinion, these ports should be left. Of course, the strength of the drive is its excellent performance. But external hard drives have another advantage: portability. If you want to transfer data using the Seagate drive to another PC, then it must have an eSATA port. Most likely, you will encounter the absence of one. It is important to understand that eSATA and SATA connectors are different from each other. You will not be able to connect ordinary SATA drives to the eSATA controller, and vice versa, connect Seagate eSATA through a regular SATA connector on motherboard.
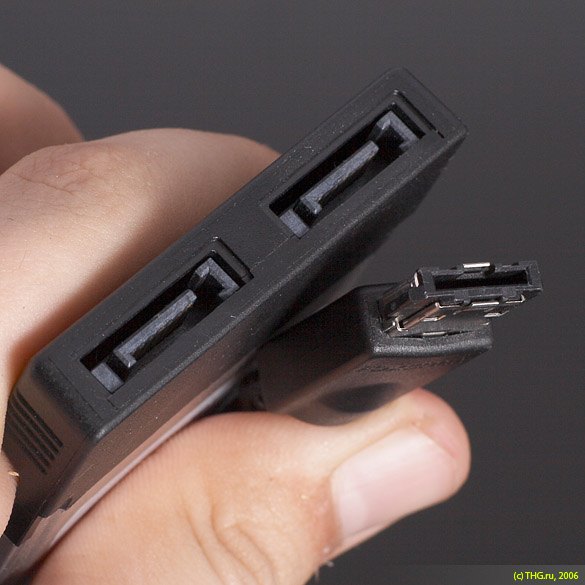

You will not be able to plug an eSATA drive into a SATA connector.
SATA and eSATA connectors on controllers.
![]()
SATA and eSATA connectors.
And yet, eSATA is gradually appearing even in low-cost motherboards. So recently a desktop computer visited the THG lab
27. 05.2017
Blog of Dmitry Vassiyarov.
SATA connector - type and characteristics of the interface
Good day dear friends.
You often see the phrase "SATA interface", your friends talk about it, but you have no idea what it is? Then you should read this article, from which you will get the answer not only to this question, but also learn how to understand the generations of this family of connectors.
Debriefing
Let's start with what an interface is. It is a means of communication between two devices; in this case, between the motherboard and hard drive. It consists of a controller, signal lines and a special protocol - the rules by which this type of interface works. To make it clearer, physically it is a connector in the motherboard where the HDD is inserted.
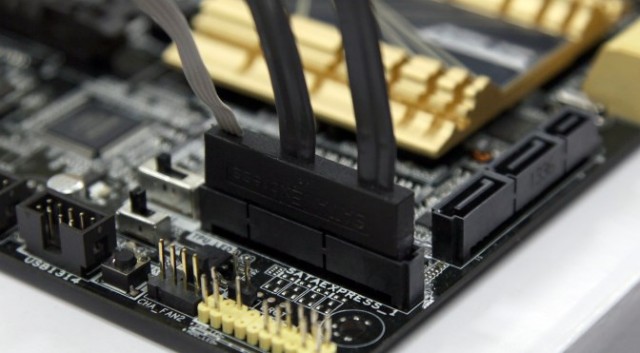
SATA on English language stands for Serial Advanced Technology Attachment, which translates as “serial application the latest technologies". The first word in this case plays a key role, since it is it that determines the type of this interface - it is sequential.

This means that data is transmitted bit by bit - one at a time - for a certain period of time. I focus on this not by chance, because the predecessor of SATA is PATA (IDE) - a parallel interface that transmitted information several bits at once. It is currently considered obsolete and therefore not in use.
The development of Sat started in 2000 by the leading companies in the computer market of that and present time, including Dell, Seagate, Maxtor, APT Technologies, Quantum, etc. They began to integrate the connector into motherboards everywhere in 2003.
Advantages
SATA is considered better than PATA in that it transfers information faster and has a thinner wire. Another plus is the reduced operating voltage due to the reduced number of contacts and microcircuits, so the controllers generate less heat, therefore, do not overheat and last longer.
Judge for yourself, SATA has 7 pins, while PATA had 40. Also, the improved shape of the cable makes it resistant to multiple connections.
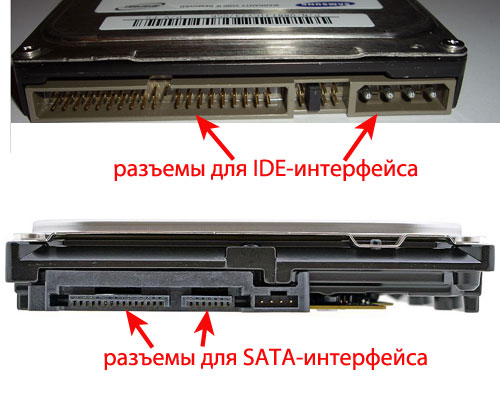
In addition, the outdated interface involved connecting 2 devices to one loop, while the modern one has separate wires for each gadget. Thus, all devices can work simultaneously, delays in data transmission are eliminated and possible problems when assembling components.
Types of SATA
To work with any SATA interface, 2 cables are used: 7-pin for information exchange and 15-pin for power connection. Instead of the latter, a Molex connector with 4 pins can be used. The power cable delivers 5 and 12 V. The wire width is 2.4 cm.

The differences between the types are in the data transfer rate and the frequency of the bus. Consider the existing generations:
- SATA. The model that came out first. Now practically not used. Its bus operated at a frequency of 1.5 GHz, due to which the throughput did not exceed 150 Mb / s.
- SATA 2. The interface first appeared in 2004 on the nForce 4 chipset of the NVIDIA brand. Externally: the same as the previous version. The frequency has been increased to 3 GHz, which increased the speed of information exchange up to 300 Mb/s.
- SATA 3. The release took place in 2008. By tradition, the performance has become 2 times greater (600 MB / s). Compatibility between devices designed for previous generations has been preserved.
After the release of this interface, 2 more modifications were released:
- 3.1 (2011). From the innovations: Zero-power optical drive (does not consume energy in sleep mode), mSATA (connector for portable and solid-state hard drives, netbooks and mobile gadgets), Queued TRIM Command (increases the productivity of SSD drives), Hardware Control Features (performs host identification of device capabilities). The data is transferred at the same speed as in the 3rd generation.
- 3.2 - SATA Express (2013). There was a merger of this family and PCIe, that is, an interface for software compatible with SATA, but the carrier connector is considered PCIe.
Physically this model designed as two side-by-side SATA ports, so you can simultaneously connect devices designed for interfaces of previous generations and - directly for Express. The data transfer rate has increased significantly: up to 8 Gb / s if 1 connector is used, and up to 16 Gb / s - if both.

eSATA
This type of interface should be singled out in a separate group, because it is intended for connecting devices from the outside. This is indicated by the first letter in the name, which carries the concept of "External" (external). The connector appeared in 2004.
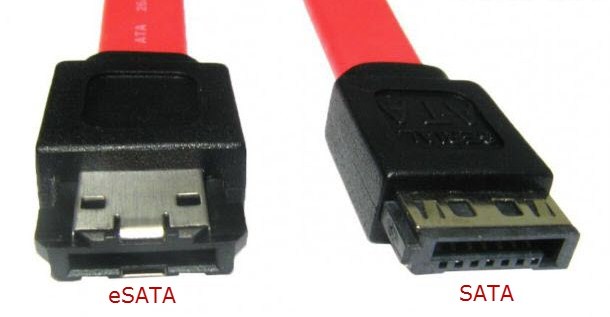
Compared to the first generation SATA:
- More reliable performance;
- The wire is extended from 1 m to 2 m;
- Various signal levels are used.
The downside of this version is the need for a special cable to connect gadgets. The disadvantage is eliminated in the next modification - eSATAp - by introducing USB 2.0 technology, while information is transmitted over wires with a voltage of 5 and 12 V.
Determining the version of the interface
How to find out which SATA connector your motherboard and devices connected to it have? There are several ways to do this:
- read specifications your model in the instructions or on the official website.
- View the inscriptions directly on the motherboard.
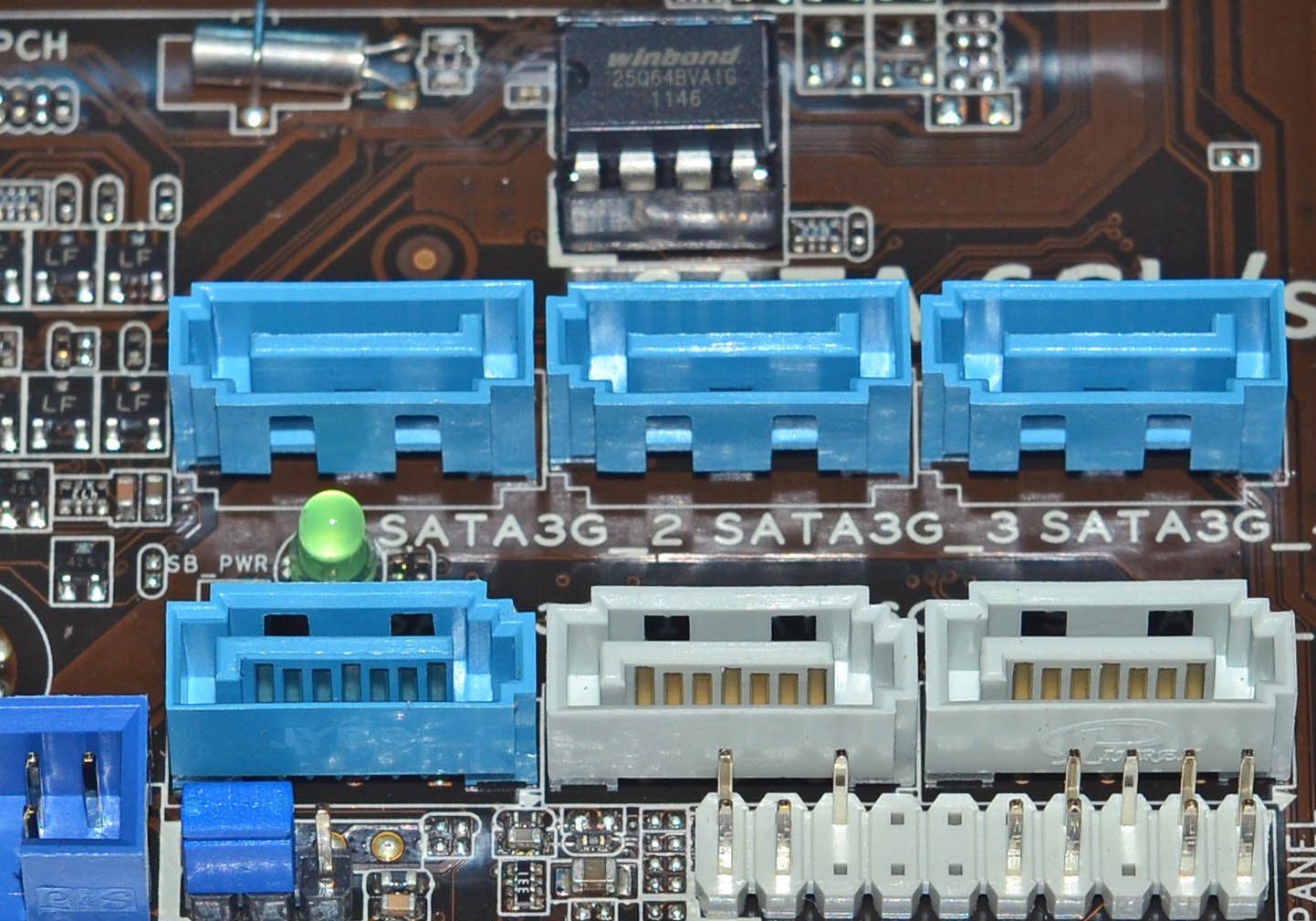
- Use the CrystalDiskInfo utility. You do not need to install it - run the .exe file from the archive. A window will open with complete information about your hardware.
Here is the site of this program: http://crystalmark.info/software/CrystalDiskInfo/index-e.html
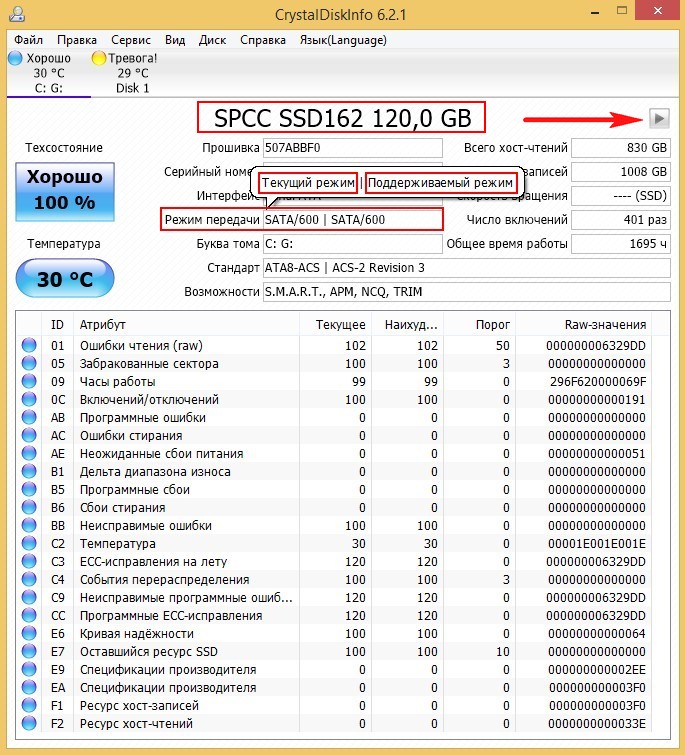
If you are going to buy a new screw, but the model you like does not fit the connector on the motherboard, do not rush to give up your choice, as special adapters are sold.
I look forward to seeing you again on my blog pages.
