The port scanner allows you to quickly check the most popular ports on your computer. Scanning lasts less than a minute, after which the result will be displayed in the form of a table.
It is worth noting that with such an express scan, the time allotted for connecting to a port is less than with a regular port check.
What ports are checked?
Below is a table of ports, with a description of the protocols that the port scanner will check.| № | Port | Protocol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | FTP Data | File Transfer Protocol - file transfer protocol. Data port. | |
| 21 | FTP Control | File Transfer Protocol - file transfer protocol. Command port. | |
| 22 | SSH | Secure SHell - "secure shell". Operating system remote control protocol. | |
| 23 | telnet | Terminal NETwork. Protocol for implementing a text interface over a network. | |
| 25 | SMTP | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is a simple mail transfer protocol. | |
| 42 | WINS | Windows Internet name service. A service for mapping NetBIOS computer names to host IP addresses. | |
| 43 | WHOIS | "Who is". Protocol for obtaining registration data about owners of domain names and IP addresses. | |
| 53 | DNS | Domain Name System - domain name system. | |
| 67 | DHCP | Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - dynamic host configuration protocol. Getting dynamic IP. | |
| 69 | TFTP | Trivial File Transfer Protocol is a simple file transfer protocol. | |
| 80 | HTTP/Web | HyperText Transfer Protocol is a hypertext transfer protocol. | |
| 110 | POP3 | Post Office Protocol Version 3 - receiving protocol Email, version 3. | |
| 115 | SFTP | SSH File Transfer Protocol. Secure data transfer protocol. | |
| 123 | NTP | Network Time Protocol. A protocol for synchronizing the computer's internal clock. | |
| 137 | NetBIOS | Network Basic Input/Output System. A protocol for providing network I/O operations. name service. | |
| 138 | NetBIOS | Network Basic Input/Output System. A protocol for providing network I/O operations. Connection service. | |
| 139 | NetBIOS | Network Basic Input/Output System. A protocol for providing network I/O operations. Session service. | |
| 143 | IMAP | Internet Message Access Protocol. Application layer protocol for accessing email. | |
| 161 | SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol - simple protocol network management. Device management. | |
| 179 | BGP | Border Gateway Protocol, border gateway protocol. Dynamic routing protocol. | |
| 443 | HTTPS | HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure is an HTTP protocol that supports encryption. | |
| 445 | SMB | server message block. A protocol for remote access to files, printers, and network resources. | |
| 514 | syslog | system log. A protocol for sending and logging messages about ongoing system events. | |
| 515 | LPD | Line Printer Daemon. Protocol for remote printing on a printer. | |
| 993 | IMAP SSL | IMAP protocol that supports SSL encryption. | |
| 995 | POP3 SSL | POP3 protocol supporting SSL encryption. | |
| 1080 | SOCKS | SOCKet secure. Protocol for obtaining secure anonymous access. | |
| 1194 | openvpn | An open implementation of Virtual Private Network (VPN) technology. | |
| 1433 | MSSQL | Microsoft SQL Server is a database management system. Database access port. | |
| 1702 | L2TP (IPsec) | Protocol for supporting virtual private networks. As well as a set of data protection protocols. | |
| 1723 | PPTP | Tunnel protocol for a secure connection to a point-to-point server. | |
| 3128 | proxy | At the moment, the port is often used by proxy servers. | |
| 3268 | LDAP | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol is a lightweight directory access protocol (directory service). | |
| 3306 | MySQL | Access to MySQL databases. | |
| 3389 | RDP | Remote Desktop Protocol is a remote desktop protocol for Windows. | |
| 5432 | PostgreSQL | Access to PostgreSQL databases. | |
| 5060 | SIP | A protocol for establishing a session and transferring multimedia content. | |
| 5900 | VNC | Virtual Network Computing is a system for remote access to a computer desktop. | |
| 5938 | teamviewer | TeamViewer is a system for providing remote control of a computer and data exchange. | |
| 8080 | HTTP/Web | Alternative port for HTTP protocol. Sometimes used by proxy servers. | |
| 10000 | NDMP | Popular port: Webmin, SIP voice, VPN IPSec over TCP. | |
| 20000 | DNP | Popular port: Usermin, SIP voice. |
If you think that this online scanner is missing some port, please
In the article I present small programs that may be useful to an ordinary system administrator. Remote access, port scanning, key extraction from software and other free utilities.
Programs for remote access
"TightVNC" is a program for accessing remote computer(like Radmin, but free). It has a client-server architecture. This means that for its operation on the computer to which you want to access, you must install the server version of "TightVNC", and on the computer from which the control will be carried out - the client version.
Installs easily. Takes up little disk space. In the server version, it is possible to set a password for access. It is also possible to launch the server version at computer startup. There is only one drawback - to connect, you need to know the IP address of the remote computer on which the program is installed.
You can download "TightVNC" from the official website: www.tightvnc.com
"Ammyy" - shareware. This means that it is possible free use at home. The main advantage is that you do not need to know the IP address of the remote machine to connect. Also, "Ammyy" does not require installation, and the client and server parts are enclosed in one executable file.
To connect to a remote computer, the Ammyy program must be running on both PCs. Each copy connects to a remote server at startup and receives a unique identifier. To connect in our version, enter the identifier "Ammyy" from a remote machine. You can download "Ammyy" from the official website: www.ammyy.com

Computer port scan
A program for scanning open ports on a computer, as well as programs that use them. You can download the program from the official website of the developers www.nirsoft.net or via a direct link from my website Download
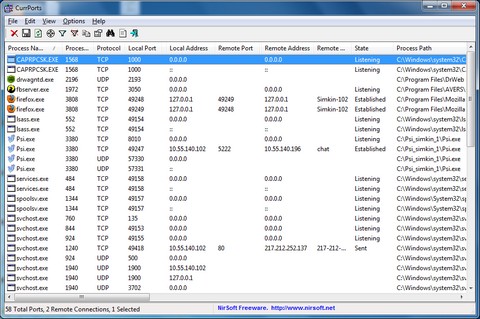
In addition, you can use the online service to check the port - open / closed. Suitable only for checking TCP ports.
Another online service that allows you to check the availability of a port on a remote machine, it is possible to select the TCP and UDP protocol.
There are also ways to check with the "telnet" and "nmap" commands entered in command line Windows.
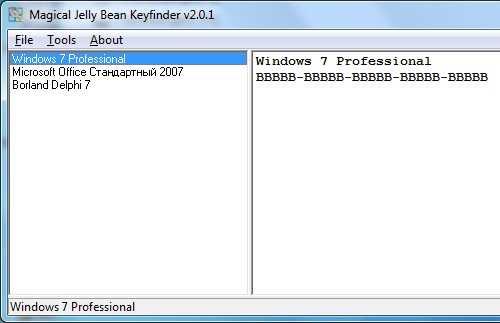
How to find out the key for the office or operating system
Sometimes you need to find out the key to the installed operating system or office from Microsoft. There is a good utility for this "KeyFinder". It displays the found keys installed on the PC software.
What is a port scan? What are the methods of scanning. What threats does it pose?
In today's article I will try to talk about what open port scanning is, I will talk about the methods used in port scanning and how to protect yourself from it all.
Scanning is a set of procedures that allows you to identify nodes, ports and services of the target system. Network scanning allows an attacker to collect a profile of the attacked machine.
According to the Ethical Hacking and Countermeasures EC-Council guidelines, the following types of scanning are distinguished:
- network scanning - determination of nodes located in the network;
- port scanning - identifying open ports and functioning services;
- System security scan - Identification of known system vulnerabilities.
At first glance, there is no harm in scanning, however, it is difficult to agree with this approach, because scanning precedes the attack, allowing the attacker to find out which services are running on the target system, and therefore prepare and conduct a targeted attack against the identified services and their vulnerabilities. Therefore, it is necessary to fight the intelligence of intruders.
Port Scan Purposes
At the same time, it would be useful to note that scanning itself is not always a malicious action, it all depends on its goals. Services information security or IT staff may well resort to scanning to find out infrastructure vulnerabilities or visibility of services from an external network.
In fact, it often starts with network scanning, it is this that allows you to identify weak nodes of their IP addresses, open ports, determine the operating system, which means that theoretically possible vulnerabilities become clear, which is not so little for the organizer of the attack.
Port Scan Methods
We reveal the structure of the network. The easiest way to scan is ICMP scanning. The principle of operation is based on the ICMP protocol, and this type of scanning allows you to find out the "live" nodes in the network and build a network diagram with a list of its nodes. The essence of the method is to send ICMP requests to network nodes, if a computer or other device working with the TCP / IP protocol stack is active, then a response will be sent. This is the so-called ping sweep or ICMP sweep. There are a huge number of tools that allow you to perform such a scan.
Port scanning. The next step is to identify open ports. In essence, this makes it possible to determine which services are running on a remote host, the list of which we have already received as a result of the previous scan. In addition, from the analysis of the received packets, you can also identify the operating system and a number of other important parameters(the presence of a packet filter, for example).
Here we are talking about TCP Scan. Its principle is based on the peculiarities of TCP operation. In essence, a very similar mechanism of interaction is adopted in aviation during negotiations between pilots and the controller, including a request, a response with an indication, confirmation of the received instruction. Such a method of interaction, if not completely eliminating the possibility of misunderstanding, then at least significantly reduces such a probability.
It could look like this:
- Pilot: Sheremetyevo-Taxiing, Aeroflot 502, clear for preliminary.
- Dispatcher: Aeroflot 502, 25 right 1 on RD2 10, highway, RD5 preliminary permission.
- Pilot: Aeroflot 502, 25 right, on taxiway 10, highway, taxiway 5 preliminary cleared.
What's going on here? The pilot turned to the controller with a request for taxiing permission and his route. The dispatcher allowed taxiing and determined the route.
The pilot confirmed the route and permission of the dispatcher. Everything, you can move - the route is received.
A very similar thing happens in TCP communication. It uses a three-way-handshake or “three-way” negotiation scheme, and the term “three-way handshake” is also found, which allows you to synchronize the transmitting and receiving nodes and establish a session, which is essentially identical to the example with radio conversations.
Using this legal algorithm, an attacker can find out which ports are open on the server, that is, to understand what services are used in the system, what operating system. To do this, there are several effective methods.
Full Connect Scan
Some port scanning techniques. The most efficient and uncomplicated scanning method is Full Connect Scan (Full Open Scan). Its principles are shown in Figure 3. An attempt is made to perform a three-way handshake with the nodes of interest to the researcher. If the desired port is open, then we receive a SYN + ACK message from it, after that we send RST to the node (session reset), if it is closed, then we receive RST from the node being checked. It should be noted that this method of scanning is easily identified, therefore, it is not difficult to resist it.
stealth scan
Another network scanning method is called Stealth Scan (Half-open Scan). In this case, the attacker tries to bypass the firewall protection and disguise itself as normal network traffic in order to avoid fixing the scan event in the system logs. Here we are not talking about negotiation, the researcher simply sends a SYN packet to the port of interest on the required server. If the response is SYN+ACK, then the port is open; if RST, then the port is closed.
This method of scanning is more sophisticated, but modern intrusion prevention systems must be able to counter it.
Xmas Scan
No less well-known scanning methods are Xmas Scan and Null Scan, however, we will not consider them due to the fact that protection against them is implemented within modern Microsoft operating systems, so they will not be of great interest to us. A feature of these types of scanning is the stealth mode of operation, that is, without setting up a session. However, you can see the details in the Ethical Hacking course or in the book "Network Security Test Lab". These types of scans are only effective on operating systems where the TCP stack is based on RFC 793. All modern operating systems from Windows Vista and older are not at risk.
Idle Scan
Perhaps the most interesting scanning method is Idle Scan. The main idea is that an attacker can scan the victim without showing him his IP address, that is, from the point of view of the scanned host, the attacker does not seem to communicate with him. A “dummy” node is used, which can be identified by intrusion countermeasures systems as a source of attack. This is a very reasonable technique, the so-called spoofing, when the sender's address is replaced with the address of another device. I must say that a computer that has certain vulnerabilities can become a "dummy" node or "zombie". Operating systems, as a rule, must be updated, but this is not always the case, and the attacker can always find "helpers", in addition, as a "zombie" can be used network printer or other network device that works with the basic functionality of the TCP/IP stack.
This scan uses the Identification field in the IP header (IPID). The IPID value increases by one in each next packet that the host sends. In essence, this is a vulnerability, since it becomes possible to predict how many packets were transmitted between the two packets that were received. Modern operating systems use a random value for the IPID field, however, as mentioned above, a solution can always be found. For modern Unix and Windows systems from Windows Vista and older, this problem has already lost its relevance.
Consider Figures 4 and 5. In the first step (1), the attacker accesses a rogue device with a standard SYN packet. The device responds with a SYN ACK (2) or SYN RST packet, which is more likely, but the IPID becomes visible to the attacker from the packet header. This is what you need to remember (3). Next, the attacker accesses the server of interest to him (4), while replacing his IP address with the address of a dummy host, that is, masking himself using spoofing (address spoofing). In response to this request, the server, if the port is open, sends a SYN/ACK to the spoofed address (5). We've made the change. Not knowing what to do with this packet, the rogue computer will respond by sending a RST (session reset) and incrementing its IPID. In our case, it will become equal to 30132 (6). If the port is closed, the server will send a session reset (RST) - see Figure 5(5).
Idle scanning (server port open)Idle scanning (server port closed)
The IPID of the dummy node remained unchanged, in our case 30131, because the "zombie" did not send anything to anyone else. Now it remains to turn to the “zombie” again, as we did above, to identify its IPID, compare it with the value we have. If the IPID has increased by 2, then the port is open.
Another important point that I would like to note is that operating systems have their own specifics when working with the TCP / IP stack. Using these features when analyzing packets received during scanning, it is quite possible to find out which OS we are dealing with, Banner Grabbing scanning techniques are built on these principles. The task is to reveal information about the computer system and its vulnerabilities, which will allow the attacker to use this knowledge for their subsequent destructive actions. Any modern scanner will provide the attacker with this information.
Operating systems usually need to be updated, but this is not always the case, and the attacker can find "helpers", in addition, a network printer or other network device that works with the basic functionality of the TCP / stack can be used as a "zombie" IP
It is easy to see that all the considered scanning methods are based on the normal behavior of nodes, which means that any computer or other network device is potentially vulnerable.
An attacker has the ability to collect and analyze the information received about the network structure, services, and system vulnerabilities. This provides a potential opportunity to prepare a targeted attack against certain nodes and services.
If you need to scan the ports of computers and devices from Windows in local network or online, then one of the best options is a bundle of Nmap and Zenmap (a GUI for Nmap).
Nmap has a large number of scan options, and Zenmap's graphical user interface makes it extremely easy to use.
Nmap features include:
- port scan
- definition operating system remote host
- determining services, software and their versions on a remote host
Using Nmap scripts, you can check remote hosts for vulnerabilities, weak passwords, collect certain information, look for services that allow anonymous login, and perform other tasks related to the actions of a network administrator or penetration tester.
Run the downloaded Nmap installer, in addition to the main program, it will also install several components that are necessary for Nmap to work on Windows.
When everything is ready, a shortcut to the program will appear on the desktop:
The main program window looks like this:
In field Target you need to specify the site address (URL), IP or range of IP addresses to be scanned.
In field Profile select the desired profile from the drop-down list.
How to Specify Target in Zenmap (Nmap)
Website addresses should be specified without a protocol, for example:
- mi-al.ru
- suip.biz
It would be incorrect to indicate the form https://mi-al.ru
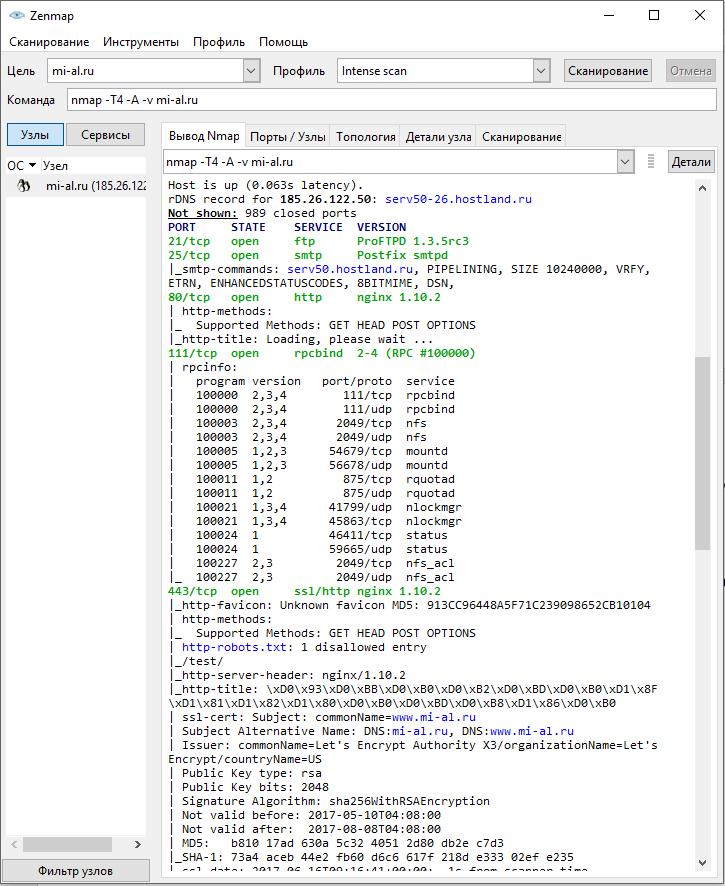
IP addresses can be specified one by one, for example, 192.168.0.1; using CIDR addressing, for example, 192.168.0.1/24; as well as specifying ranges in one or more octets, for example, 192.168.0.1-100, or 192.160-170.50-100.1
What do Profiles mean in Zenmap
Profiles in the main Zenmap window are a set of options for typical scans. Consider all Zenmap profiles.
- intensive scan(Intensive scan)
Intensive all-round scanning. Option -A includes several other options at once: OS version detection ( -O), determining the versions of running services ( -sV), scanning using scripts ( -sC) and tracing ( --traceroute). Without administrator privileges, only version detection and scripted scanning are launched. This is considered an intrusive (intrusive) scan.
- intensity scan plus UDP(Intensive scanning plus UDP)
Makes OS detection ( -O), version detection ( -sV), scanning with scripts ( -sC) and tracing ( --traceroute) in addition to TCP and UDP port scanning.
- Intense scan, all TCP ports(Intensive scanning, all TCP ports)
Scans all TCP ports, then does OS detection ( -O), version detection ( -sV), script scanning ( -sC) and tracing ( --traceroute).
- Intense scan, no ping(Intensive scanning without ping)
Performs an intensive scan without first checking if the targets are working. This can be useful when targets ignore normal host discovery probes.
- ping scan(ping)
This scan only determines which targets are running and does not perform a port scan.
- Quick scan(Quick scan)
This scan is faster than a normal scan because it uses an aggressive timing pattern and scans fewer ports.
- Quick scan plus(Quick scan plus)
Quick scan plus OS detection
- Quick traceroute(Quick trace)
Traces paths to targets without performing a full port scan on them.
- regular scan(Normal Scan)
Basic scanning without additional options.
- Slow comprehensive scan(Slow all-around scan)
This is a comprehensive, slow scan. Every TCP and UDP port is scanned. OS detection in progress ( -O), version definition ( -sV), script scanning ( -sC) and tracing ( --traceroute). Many probe requests are sent to discover hosts. This is a very intrusive scan.
For example, if I want to know which subnet hosts are being pinged, then I choose the profile ping scan.
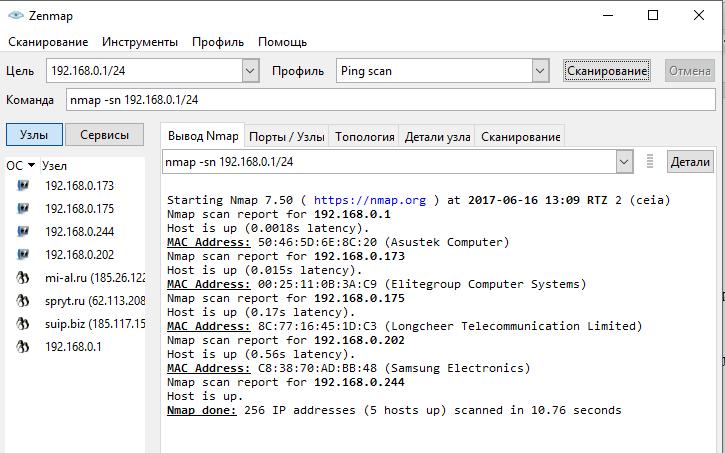
With the user-friendly profile editor, you can edit and create new profiles.

Although using the profile editor contains a description of the actions to be performed and therefore does not require knowledge of Nmap options, for a deeper understanding of the program, you can read the description of all Nmap options at https://kali.tools/?p=1317
If you want to scan all TCP ports, then specify the target and enter as a command nmap -p 1-65535

Scan results
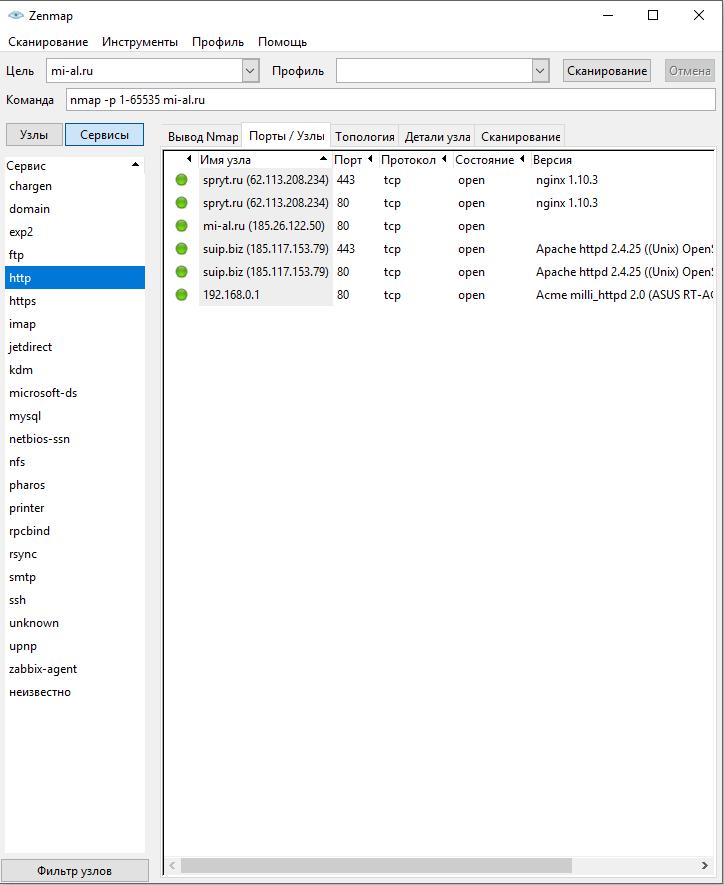
The results obtained from the last scan are visible in the tab Output nmap. On the left side you can switch between knots and Services. When you click on a specific node, you will see the previous scan results. When you click on a service, you will see the nodes where the service was discovered:
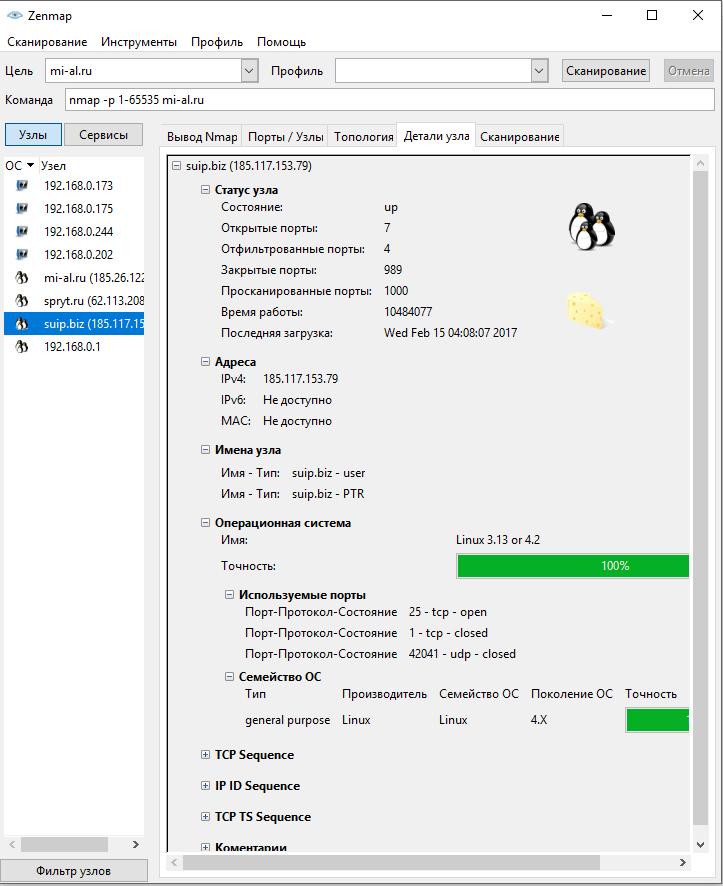
To view generalized information on a node, click on it and select the tab Node details:
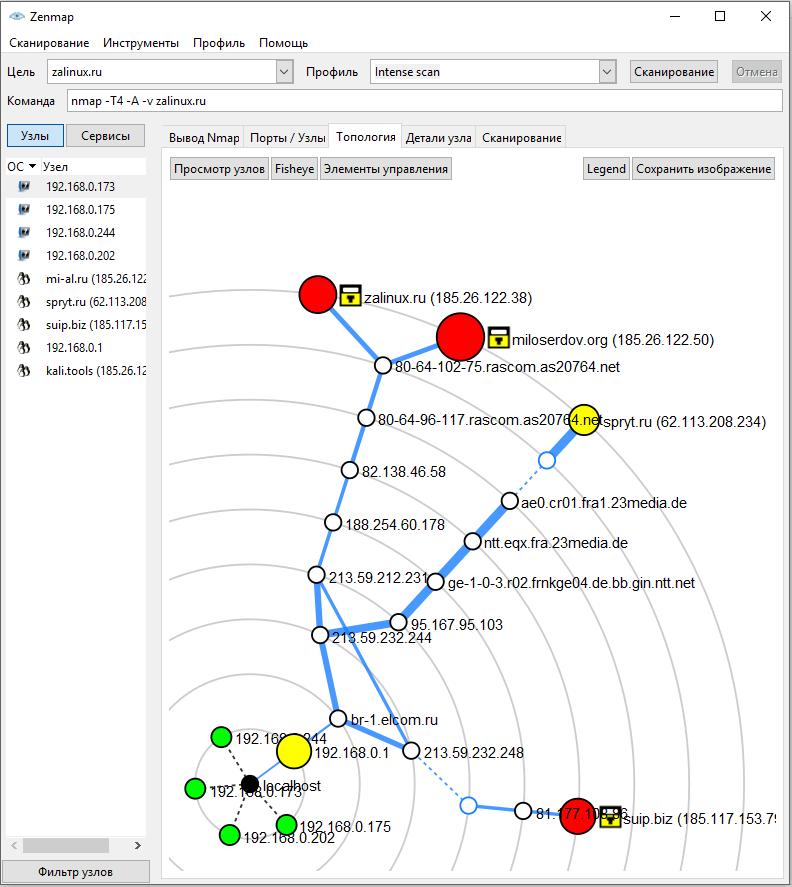
In the tab Topology you will see information about connections between scanned/discovered nodes:
Using Nmap on Windows at the Command Line
If you need a console version of Nmap, then you can use it on Windows just as you would on Linux. When installing Nmap, it adds the path to the Nmap executable file to the environment variables, so on the command line you just need to specify the name of the program:
Conclusion
Nmap allows Windows to scan computers and other devices for open ports. It is also able to determine the services running on a remote host, their version.
The graphical interface makes it easier to use the program, but it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with all the options of the program in order to gain skills in various scanning techniques.
In addition to their main functions - scanning ports and determining the versions of installed software - Nmap scripts allow you to perform various other tasks, including checking for vulnerabilities, weak passwords, and collecting information.
